Introduction
Ethylestrenol and stanozolol are anabolic steroids which can be used to increase muscle mass and enhance performance. These drugs have been linked to instances of doping in race horses. This application note describes a Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) protocol for the extraction of ethylestrenol and stanozolol from horse urine prior to LC-MS/MS analysis.
The method described in this application note achieves high reproducible analyte recoveries from both gelding and filly urine. Protocols for 48-well, 96-well plate and column formats are described.
ISOLUTE® SLE+ Supported Liquid Extraction plates and columns offer an efficient alternative to traditional liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) for bioanalytical sample preparation, providing high analyte recoveries, no emulsion formation, and significantly reduced sample preparation.

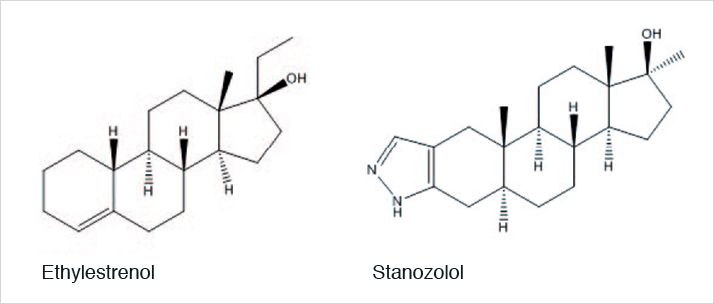 Figure 1. Structures of Ethylestrenol and Stanozolol
Figure 1. Structures of Ethylestrenol and StanozololAnalytes
4-Ethylestrenol and Stanozolol.
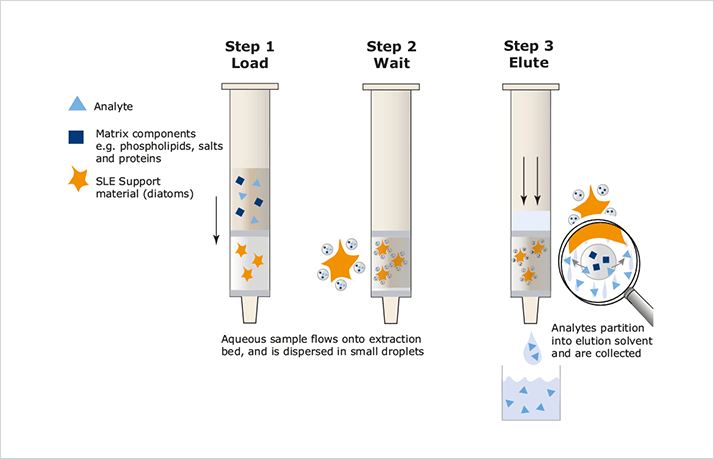 Figure 1. Supported liquid extraction mechanism.
Figure 1. Supported liquid extraction mechanism.Sample Preparation Procedure
Format: ISOLUTE® SLE+ 1 mL Supported Liquid Extraction plate, 48-well, part number 820-1000-Q01. Protocols for 96-well plates and column formats are also included, see Table 1. Sample Pre-treatment Take appropriate volume of urine and add same volume of H2O. Mix. Sample Loading ISOLUTE SLE+ 48-well plate: Load the pre-treated sample (800 μL) to each well of the 48-well plate followed by a pulse of vacuum or positive pressure to initiate flow. Leave to absorb for 5 minutes. Elution Ensure a suitable collection vessel is in place. Apply 1 mL of MTBE and allow to flow under gravity. Apply a second 1 mL of MTBE and allow to flow under gravity. Apply a third 1 mL of MTBE and allow to flow under gravity until the solvent reaches the top frit. Pull through the remaining solvent with vacuum or positive pressure for 10–20 seconds. Note: DCM is a suitable alternative elution solvent Post Elution Evaporate to dryness at 40 °C in a stream of air or nitrogen. Reconstitution* Reconstitute using 500 μL of 20/80 H2O/ACN with 0.1% Formic acid. Mix gently. *Recovery and reproducibility for ethyestrenol was found to be affected by non-specific binding and/or losses on evaporation and reconstitution. We recommend that collection vessels, evaporation vessels and reconstitution solvents are investigated during method development to minimize losses/variability.





