Introduction
Size exclusion chromatography (sec) is the standard method for aggregate and fragment analysis of monoclonal antibodies in biopharmaceutical qc. A new series of silica-based sec columns was engineered to provide shorter analysis time or higher resolution than standard columns for the separation of fragments, monomers and dimers.

Antibody therapeutics are enjoying high growth rates in the biopharmaceutical market, the major areas of therapeutic application being cancer and immune/inflammation-related disorders including arthritis and multiple sclerosis. In 2010, four of the top ten best-selling global drug brands were monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The characterization of these complex biomolecules is a major challenge in process monitoring and quality control. The main product characteristics to be monitored are aggregate and fragment content, glycosylation pattern and charged isoforms. The standard method used in biopharmaceutical QC for mAb aggregate and fragment analysis is size exclusion chromatography (SEC). A new series of silica based HPLC columns can be applied to either increase speed or improve resolution of the separation of antibody fragments, monomers and dimers.
Experimental
IgG was digested with papain over 24 hours. The fragmentation process was monitored by analyzing 10 or 5 μl aliquots of the sample.
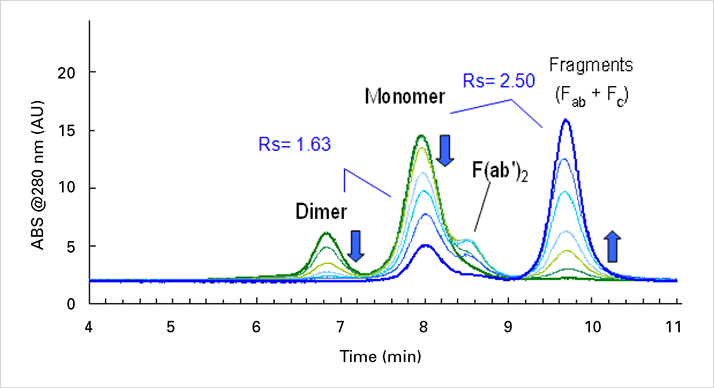 Separation of mab fragments, monomers and dimers
Separation of mab fragments, monomers and dimers




