Introduction
Pesticides are frequently found as contaminations in food and environmental matrices. They commonly are analyzed by GC-MS or LC-MS. Both are complementary, “orthogonal” methods, comprising in total >1100 known pesticides. While they overlap in scope, each method alone covers exclusively a certain range of pesticides: GC-MS is more common for semi-volatile compounds, LC-MS is favorable for polar and thermo-labile pesticides. Full scan accurate mass screening with atmospheric pressure inlet LC-MS has become increasingly popular in recent years. It is able to cover hundreds of target compounds in a single run and additionally enables the identification of unknowns and retrospective analysis. Target compounds are identified by their retention time, mass accuracy and isotope pattern. Reliability of identification is improved by using diagnostic ions generated by broadband CID alternating with full scan data acquisition. Diagnostic ions are valuable in complex matrices as they support the differentiation of target analytes signals from the matrix background.

Here we describe for the first time the application of bbCID data acquisition for pesticide target screening by coupling a GC to an atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source (GC-APCI) and a high resolution QTOF-MS.
Methods
For this GC-APCI-MS screening study a mix of 60 representative pesticides was chosen with regard to their relevance to routine screening. The mix was diluted in dichloromethane to appropriate concentrations for the generation of calibration curves between 0.01 ng/ml (0.01 pg/μl) and 1000 ng/ml. Samples were prepared by spiking 10 pg and 50 pg of the pesticide mix into 1 ml QuEChERS extracts of orange, peach and tomato. For all analyses 2 μl of each sample were injected into the GC. GC-MS analysis was performed using a 450-GC with PAL Combi-xt Autoinjector coupled with a GC-APCI II source to an impact II QTOF mass spectrometer (all Bruker Daltonics). The GC was operated with a 30 m Rxi-5ms capillary column (0.25 mm ID, 0.25 μm film thickness), operated at 1.2 ml/min constant helium flow and a GC oven temperature program at 70°C (1 min) - 25°C/min - 180°C - 15°C/min - 300°C (8.1 min). Pulsed splitless injection was at 280°C (40 psi for 0.25 min, 1 min splittless time).
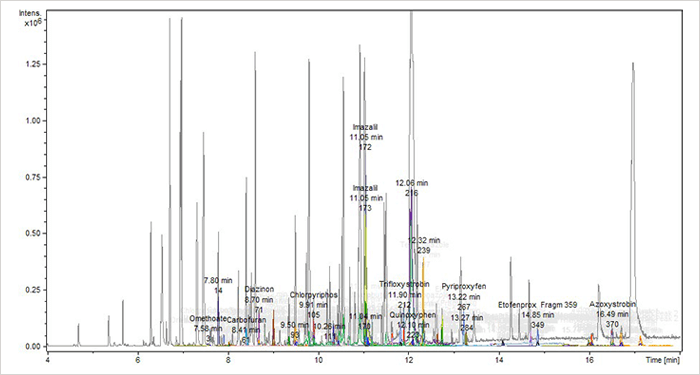 Figure 1: Base Peak (grey BPC) and Extracted Ion Chromatograms (EIC) of 48 pesticides in peach QuEChERS extract (50 ng/ml each): BPC shows a complex peak pattern of non-target matrix substances.
Figure 1: Base Peak (grey BPC) and Extracted Ion Chromatograms (EIC) of 48 pesticides in peach QuEChERS extract (50 ng/ml each): BPC shows a complex peak pattern of non-target matrix substances.




