Introduction
Bile acids are increasingly recognized as playing an important signaling role in the control of immune response and energy metabolism. Recently, there has been interest in measuring bile acid concentrations in plasma and their impact on hormone concentrations, for example as affected by bariatric surgery (Figure 1).
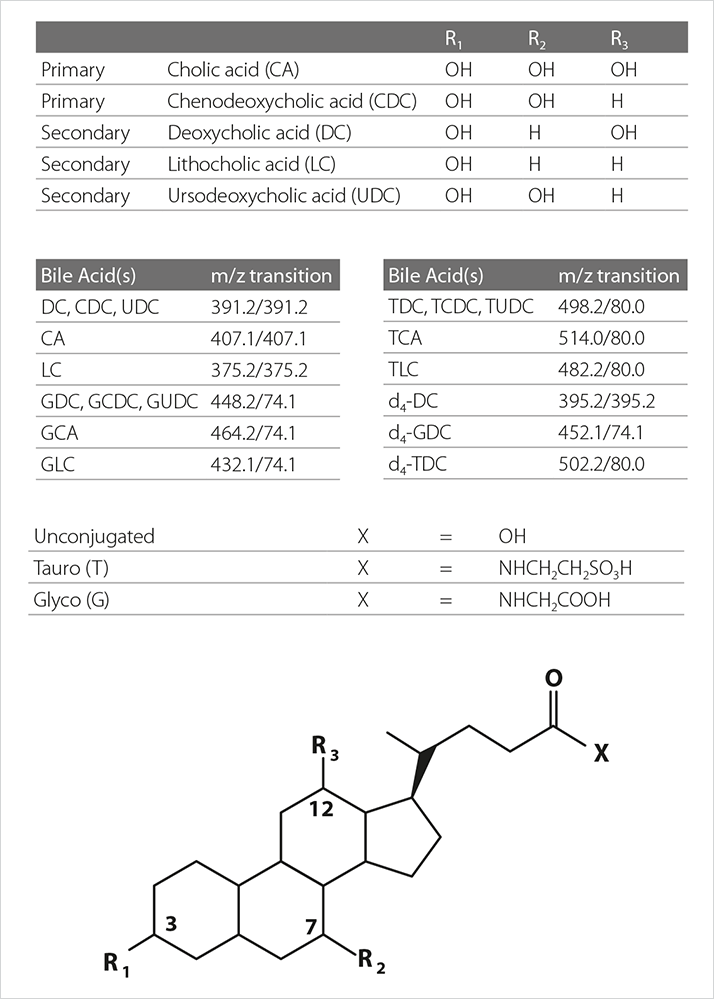
Primary bile acids are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol. The majority are conjugated, increasing hydrophilicity, with either glycine or taurine. They are stored in the gall bladder and released into the small intestine on food consumption. Bacteria in the gut can convert primary bile acids to secondary bile acids which are then reabsorbed and taken back to the liver as part of enterohepatic circulation. Here secondary bile acids can also be glycine or taurine conjugated. Spill-over from this system results in bile acids in the peripheral circulation. There are potentially 15 species which can be measured in a peripheral plasma sample (Figure 2).

Methodology
The quantitation of plasma bile acids by tandem mass spectrometry MS/MS presents an analytical challenge. When employing collision-induced dissociation, bile acids will either form no useful fragments for quantitation (unconjugated), or produce a charged fragment originating from a conjugation group (conjugated taurine and glycine salts).These are two possible options for reducing dietary food intake. Both procedures create a small pouch at the start of the stomach by either restricting the stomach with a gastric band or by surgically creating a separate pouch from the stomach and then attaching it to the remainder of the GI tract.
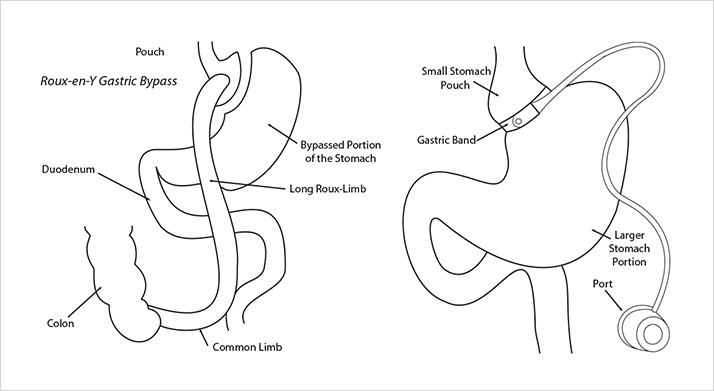 Figure 1. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Gastric Banding
Figure 1. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Gastric BandingThese are two possible options for reducing dietary food intake. Both procedures create a small pouch at the start of the stomach by either restricting the stomach with a gastric band or by surgically creating a separate pouch from the stomach and then attaching it to the remainder of the GI tract. As three of the bile acids have the same molecular weight and elemental composition, they cannot be differentiated by MS/MS alone and require chromatographic separation of the group in both their unconjugated and conjugated forms. To enable separation, several orthogonal HPLC stationary phases were screened for selectivity. The best separation was achieved with an Ascentis Express C18 analytical column based on Fused-Core® technology.