Jeff Op de Beeck, Geert Van Raemdonck and Paul Jacobs
The importance of establishing robust and reliable analytical methods is of paramount importance in today’s life science research and the (bio) pharmaceutical industry. Liquid chromatography (LC), e it h e r coupled with UV detection or mass spectrometry has a prominent position within biomarker discovery and quality control workf lows. Among other factors, the quality of the LC column has a significant impact on the data reproducibility and thus the method robustness. LC columns are typically fabricated by packing spherical silica particles into a cylindrical column. Even though column technology has improved enormously in the past decades, batchto-batch repeatability is still a critical issue that can have a serious impact on LC workflow robustness. By using an entirely different LC column fabrication process, PharmaFluidics brings an extremely robust alternative to the LC column market, called micro Pillar Array Columns (µPAC™).
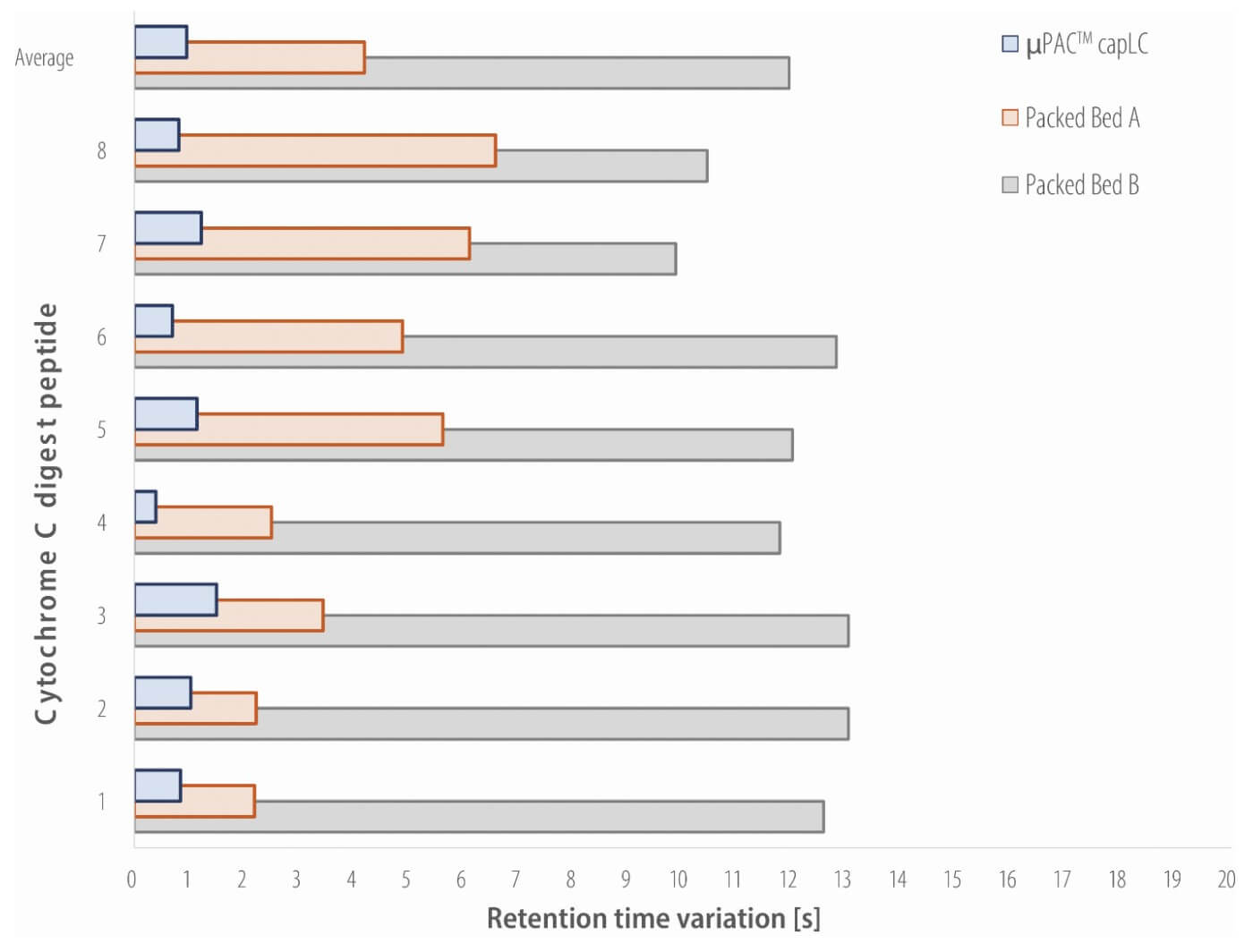
In this study the column-tocolumn reproducibility of µPAC™ columns is compared to state-of-the art commercially available packed bed column alternatives. Reversed phase capillary LC analysis of a protein tryptic digest is performed on a series of columns (three column types, n=3), and column-to-column reproducibility is compared in terms of retention time, efficiency and peak shape.
The most critical parameter when comp a r i n g colu m n-to -colu m n reproducibility is the retention time (RT) that is achieved for the different compounds in a sample. Whereas stateof-the art packed bed alternatives show absolute RT variation values in the order of 5–12s on average, sub second variation (0.95s on average) is achieved with the µPAC™ columns. This results in a relative variation in retention time of 0.24 (%CV), compared to 0.62 and 2.02 for the packed bed alternatives, which is up to three times more reproducible. Regarding efficiency, average peak widths of 0.13min were obtained for the µPAC™ column, whereas this was 0.15min for both packed bed alternatives.
In conclusion, whereas state-of-theart LC columns show RT variation values in the order of 5–12s, sub second variation was achieved with three different µPAC™ capLC columns. With values down to 0.24 percent CV on three different columns, this approaches what can be achieved on just a single conventional column, highlighting the unique potential for standardizing analytical procedures. In addition to the inter column RT consistency, excellent and consistent separation performance is demonstrated for tryptic digest samples, generating highly symmetrical peptide peaks.





