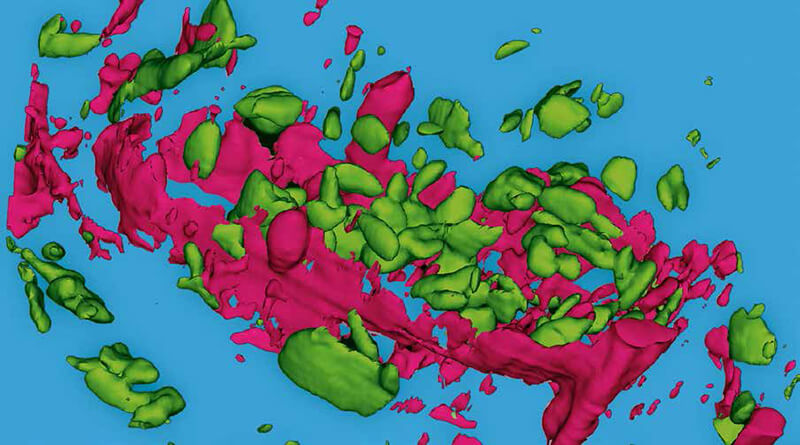
Confocal Raman microscopy is a powerful technique for highresolution, non-destructive and label-free chemical analysis. It is well-suited for three-dimensional investigation of samples from various fields of application.
Confocal Raman imaging is a microscopy technique for identifying and imaging of chemical and molecular compounds. This non-destructive, non-invasive and label-free method is used in various fields of application such as nanotechnology, materials and surface research, geological, environmental and life sciences and pharmaceutics.
The Raman effect (or Raman scattering) is based on the inelastic scattering of light interacting with molecules in a sample. This interaction causes vibrations in the chemical bonds, leading to a specific energy shift in the scattered light that is visible in its spectrum. The Raman spectrum is as unique for each chemical compound as a fingerprint and can be detected and identified by Raman spectroscopy.
For confocal Raman imaging a Raman spectrometer is combined with a confocal optical microscope. The microscope facilitates morphological characterization and establishes the spatial distribution of chemical components within a sample. High-resolution confocal Raman systems acquire the information of a complete Raman spectrum at every image pixel and achieve a lateral resolution at the diffraction limit. The confocal microscope setup is furthermore distinguished by a high signal-to-noise ratio and enables the generation of 3D Raman images and depth profiles. Additional sample characteristics such as the relative amount of a specific component, stress and strain states, or crystallinity can be further analyzed and imaged.