Introduction
A variety of products derived from monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), including mAb fragments and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), are being developed for the treatment of cancer and other diseases due to their increased potency combined with reduced toxicity. However, the efficacy of these molecules is highly dependent upon the target site-specificity and binding properties of the mAb, the linker stability, the potency of the drug, and both the distribution and number of drug species on the mAb.1 These requirements highlight the importance of characterizing these highly heterogeneous products using appropriate analytical techniques in order to assess and monitor them during manufacturing and subsequent storage.
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is a technique for protein separations and has been commonly used as an orthogonal method to size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and ion exchange (IEX) chromatography for the characterization of mAbs. Here we introduce Proteomix® HIC columns which have been designed for high resolution and high efficiency separations of proteins, oligonucleotides, and peptides.

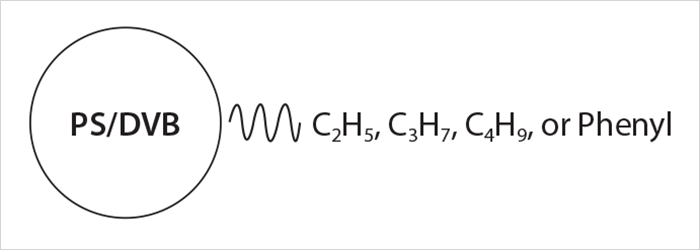 Figure 1. Structure of Proteomix HIC-NP5 Resin
Figure 1. Structure of Proteomix HIC-NP5 ResinGeneral Description
Utilizing proprietary surface technologies, Proteomix HIC-NP resin is made of non-porous polystyrenedivinylbenzene (PS/DVB) beads with narrow-dispersed particle size distribution. As shown in Figure 1, the PS/DVB bead is modified with alkyl groups or an aryl group that provides hydrophobic interaction with analytes. Proteomix HIC-NP resin is highly rigid and mechanically stable. In comparison to silica based HIC phase media, Proteomix HIC-NP phases have advantages for biomolecule separations with wide pH range (2-12) and high thermal stability. The nonporous structure and narrow particle distribution offer special selectivity, high resolution separation of proteins such as mAbs, ADCs, and related protein fragments, as well as DNA and oligonucleotides. Proteomix HIC-NP media are applicable at laboratory discovery, laboratory-scale purification, and process chromatography for the production of a few mgs to kilogram of proteins.
Featured Characteristics
- Highest capacity and resolution
- Consistent lot-to-lot reproducibility
- Improved protein recovery with intact biological activity
- Negligible non-specific interactions
- Ideal for separation and analysis of hydrophobic proteins, mAbs, and ADCs
- Suitable for separation and analysis of general biological samples





