Oligonucleotides are short lengths of DNA/RNA which are increasingly being used as therapeutic agents for the treatment of genetic disorders and cancers.
With oligonucleotide treatments, it is possible to synthesize a single-strand of DNA/RNA which has a complementary sequence to a disease-causing gene. Once this therapeutic DNA sequence has bound to the target gene in the body, the gene is deactivated. This method of treatment is known as antisense therapy
Currently, over 100 oligonucleotide-based therapies are in the clinical pipeline with many more in the pre-clinical development stage.
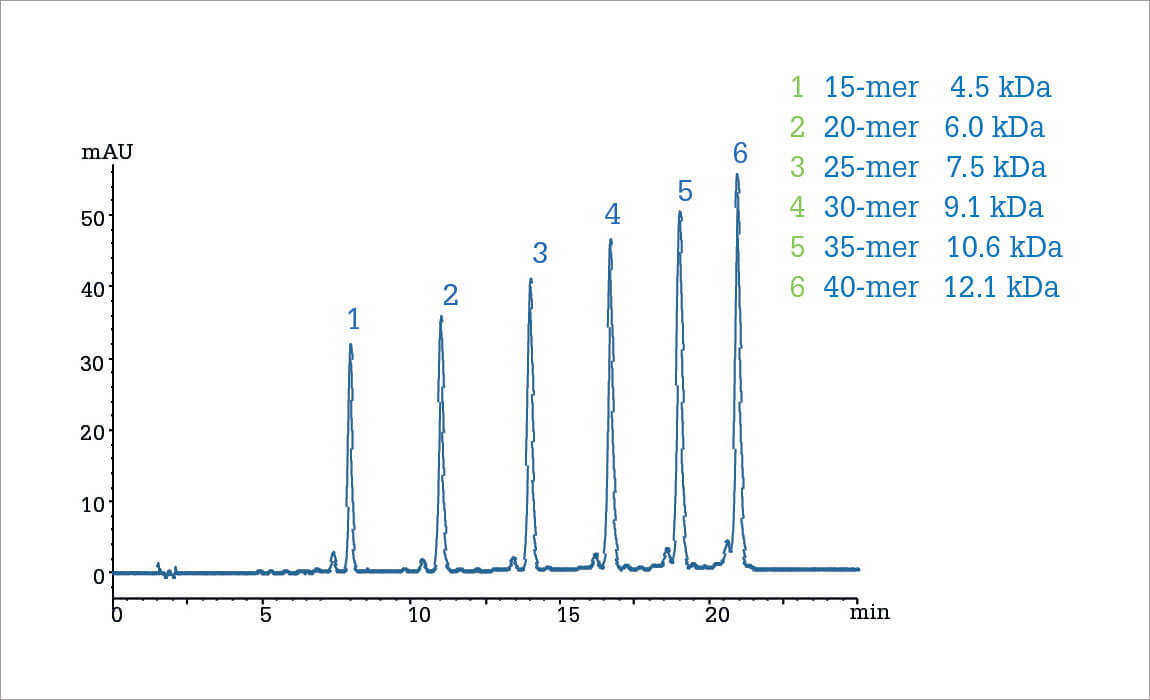
Several impurities can be produced during oligonucleotide synthesis (e.g. failure sequences), due to a less than 100 percent efficient process, and these need to be removed from the desired product.
This purification process can be performed using ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC (RPLC).
Download at https://uk.cmd.vwr.com/rq/ddl/ace_020