Introduction
HybridSPE®-Phospholipid plates provided excellent analyte recovery of these difficult compounds from plasma samples with subsequent LC/MS/MS analysis on Ascentis® Express Fused-Core® C18 columns. The extracts were free of endogenous phospholipids that can interfere with quantitation, decrease sample throughput and reduce column lifetime.

There is a growing trend toward converting some clinical methods from immunoassay to LC/MS/MS for a variety of reasons. LC/MS/MS improves assay specificity, is not limited by antibody availability, and allows multiplexed analyte assays to be conducted simultaneously. However, LC/MS/MS is not without its limitations, most notably interferences from endogenous sample matrix, which can result in seemingly random and arbitrary discrimination in analyte response, among other effects.1
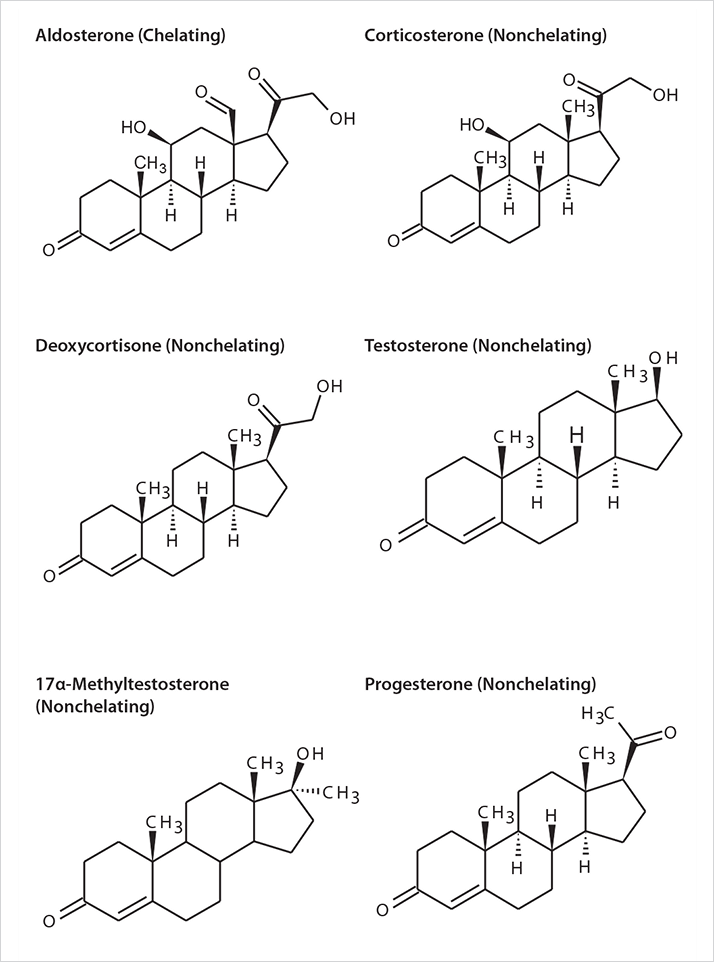 Figure 1: Steroid Hormones.
Figure 1: Steroid Hormones.Objectives of the Study
The goal of this study was two-fold. First, to develop a simple LC/ MS/MS method, including sample preparation using HybridSPEPhospholipid plates, for the direct analysis of the steroid hormones progesterone, aldosterone, corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone, testosterone, and 17α-methyltestosterone from blood plasma. Second, to compare the background from sample matrix between the resultant sample prep method to standard protein precipitation.
Experimental
Chromatographic (LC/MS/MS) Conditions
The chemical structures of the steroid hormones are shown in Figure 1. Initial evaluation was conducted using a mixture of steroid hormones to establish chromatographic conditions on Ascentis Express C18 column. The gradient profile was extended so matrix monitoring could be conducted for the processed plasma samples.
HybridSPE-Phospholipid Operating Principles
HybridSPE-Phospholipid technology combines simple, standardized methodology of protein precipitation with the specificity of solid phase extraction for the simultaneous removal of proteins and phospholipids from biological samples. The technology is based on hybrid zirconia-silica particles for targeted isolation of phospholipids, while PTFE frit materials act as a depth filter for efficient removal of precipitated protein particles. The zirconia portion of the hybrid particle behaves as a Lewis acid (electron acceptor) which interacts strongly with Lewis bases (electron donors), like the phosphate moiety of phospholipids. This technology allows for highly selective phospholipid matrix removal while remaining non-selective towards a broad range of analytes.2
Sample Prep Method Development: Factors that Impact Analyte Recovery
Sample prep method development consisted of establishing recovery of standard compounds from the HybridSPE-Phospholipid 96-well plates, then transferring those conditions for use with spiked plasma samples. Method optimization consisted of evaluating several precipitation solvent systems. Once sufficient analyte recovery was established for the plasma samples, the final portion of the study was to compare the HybridSPE-Phospholipid technique with the commonly accepted protein precipitation for phospholipid matrix removal.





