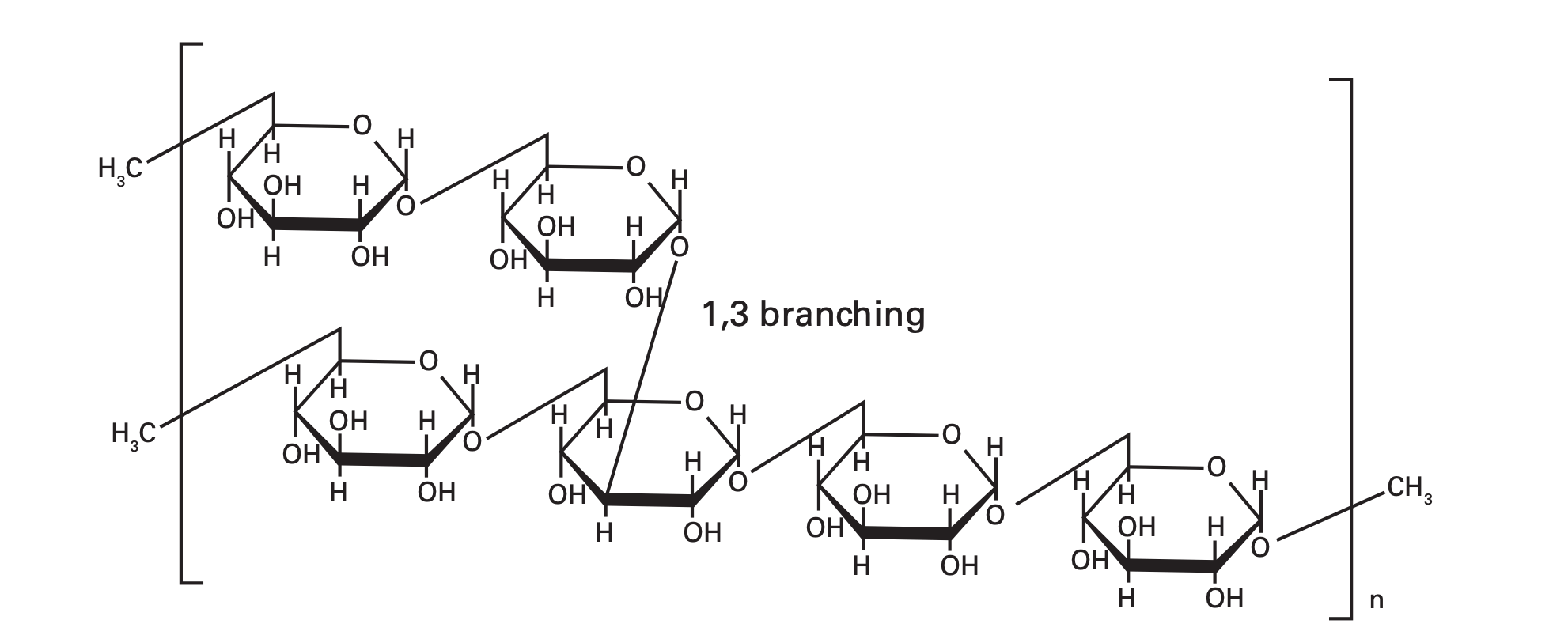
 Figure1. Structure of dextran
Figure1. Structure of dextranDextran is one of the most common representatives of polysaccharides, a macromolecule consisting of α-1,6 linkages between glucose units. In addition, α-1,3 (and infrequently α-1,2) linkages can be present, thus creating branches on the main glycan chain (see Figure 1). These materials have a remarkable diversity in physicochemical properties due to the variation in chain length and degree of branching. Dextran’s commercial applications are typically found in the food and pharmaceutical industry, such as vaccines, eye medicines, organ preservation, and blood cell separation. They are also used as blood plasma surrogates.
Pullulan is another widely studied type of polysaccharide. It consists of maltotriose units, made of three glucose monomers with α-1,4 linkages, which are connected by α-1,6 glycosidic bonds (see Figure 2). The coexistence of both types of glycosidic bonds generate an intermediate structure between dextran and amylose. This unique linear structure provides the specific structural flexibility and solubility of pullulan, resulting in distinct film- and fiberforming characteristics which are not exhibited by other polysaccharides. Pullulans have numerous uses in the food, manufacturing, electronic, and pharmaceutical industries, such as wound-healing compositions, pharmaceutical coatings, oral care products, and non-toxic conjugates for vaccines.





