In the search for extraterrestrial life, finding organic molecules has been a topic of special interest. NASA’s Curiosity rover equipped with the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) Suite Investigation in the MSL Analytical Laboratory is designed to address this interest. The main analytical chemistry hurdle that SAM resolved is using pyrolysis to 1: thermally extract organic matter with low molecular weight from a piece of inorganic matter sample, which is usually insolu ble into common solvents; 2: thermally break carbon bond in organic matter with high molecular weight; and 3: send to GC/MS for identification. As the inventor of the first commercial pyrolyzer for a GC/MS system, CDS Analytical contributed to the development of SAM in the Curiosity rover (1), which was launched on November 26, 2011 and landed on Mars on August 5, 2012.
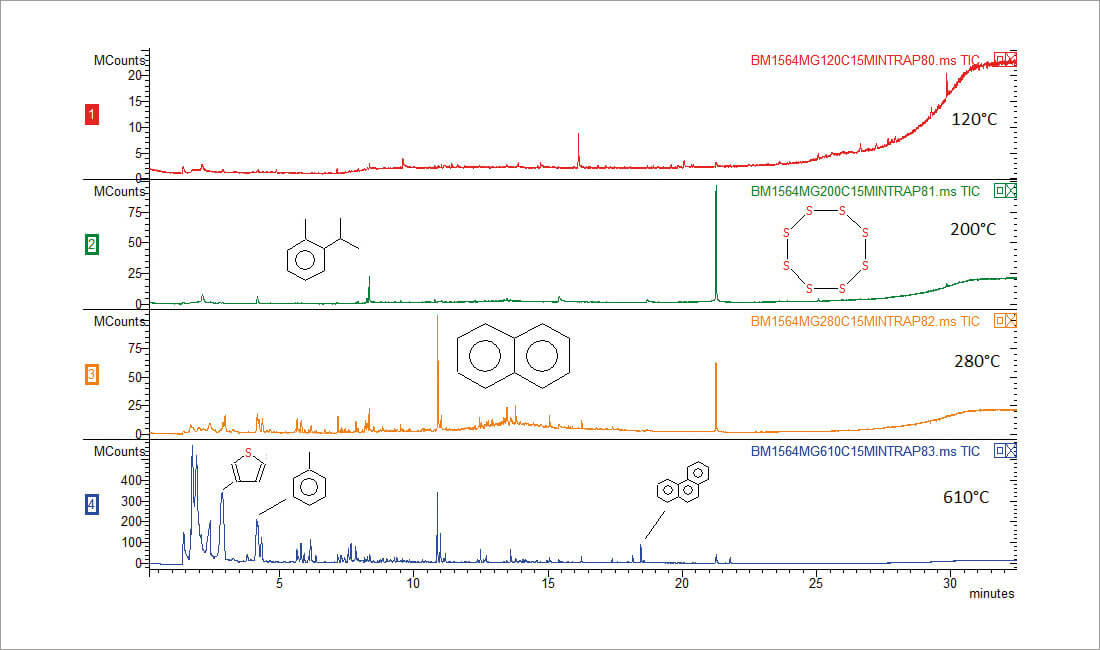
This application note demonstrates the operation of SAM by thermally extracting 15 mg of powdered meteorite in a multi-step sequence of 120°C, 200°C, 280°C, followed by a flash pyrolysis at 610°C to evaluate its organic matter content.
Experimental Parameters
A small piece from Murchison meteorite, which fell in Australia in 1969, was pow dered, and 15 mg of the powder was added to a DropIn-Sample Chamber (DISC) tube, to run on a Pyroprobe 6200.
Pyroprobe
DISC chamber: 120°C 15 min 200°C 15 min
280°C 15 min 610°C 30 sec
Trap rest: 40°C
Trap final: 300°C 4 min
Interface: 300°C
Transfer line: 300°C
Valve oven: 300°C
GC/MS
Column: 5% phenyl (30m x 0.25 m)
Carrier: Helium 1.25mL/min
25:1 split
Injector: 300°C
Oven: 40°C for 2 minutes
10°C/min to 320°C
Ion source: 230°C
Mass range: 35–600amu
Results and Discussion
All four temperature runs are summarized in Figure 1. The run at 120°C did not yield organic compounds at enough concentration to be identified. Aromatics started to emerge at 200°C, along with cyclic sulfur. At 280°C, aromatics at higher boiling point, like naphthalene and some hydrocarbons become more abundant. Sulfur compounds such as thiophenes also were extracted.
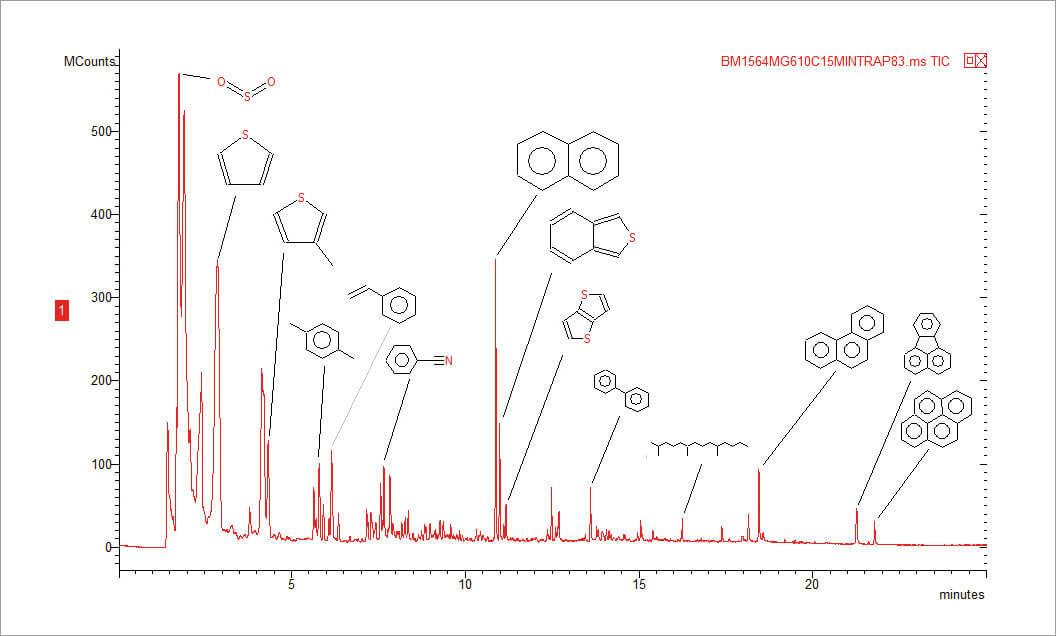
The last flash pyrolysis run at 610°C in Figure 1 was zoomed in Figure 2 to show more details. Pyrolysis at 610°C revealed sulfur dioxide, more thiophenes, hydrocarbons, and polycyclic aromat ic hydrocarbons, including phenanthrene.
This application note demonstrated thermal extraction and py rolysis analysis of powdered meteorite using a 6200 Pyroprobe with GC/MS.