The presence of nitrosamines in drug products is a continuing challenge for the pharmaceutical industry (EMA (2021); US FDA (2021)). Golob et al. (2022) have provided an excellent, up-to-date overview of the history. A method for quantitation of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) direct from drug products using headspace- selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) was described in a recent application note (Perkins and Langford (2022a)). There, two ranitidine drug products were used as part of method development. Although these were not from a recalled batch to the best of our knowledge, NDMA concentrations of 68 and 328 ng g-1, respectively, were detected.
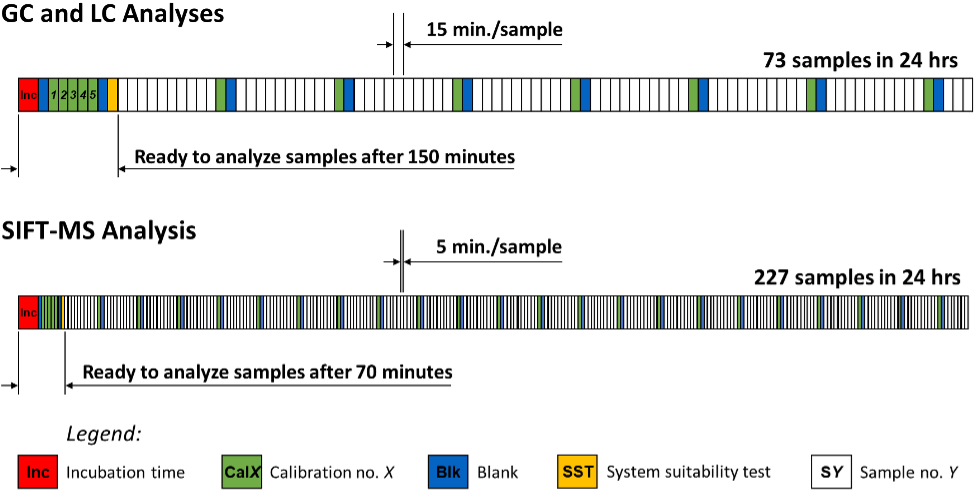
As described in the previous application note, headspace-SIFT-MS is well suited to quantitative screening of volatile nitrosamines in drug products because it is highly sensitive and selective, while providing significant advantages over routine chromatographic analysis through delivery of faster results and higher sample throughputs (Figure 1). This study applies the method developed previously to a different drug product: valsartan. The sample tested was subject to voluntary recall in July 2018 (FDA (2018a)).





