The capability of the Mastersizer 3000 and Aero S dispersion unit to measure small quantities of dry powders has been established in a separate application note [1]. Valid concerns when measuring such a small sample are that a) it is not representative of the bulk and b) small amounts of oversized particles may not be detected. Such oversized particles have the potential to cause problems with powder handling, dissolution rates and the bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients. In this application note, we demonstrate the ability of the Mastersizer 3000 and Aero S dispersion unit to detect a small proportion of anomalously large particles added to a small aliquot in a 'seeding' experiment. We have chosen a fine grade of lactose as a model for pharmaceutical API or excipient powders. This lactose has a Dv (50) of 4µm. The anomalous particles will be a known sample of glass beads with a Dv (50) of 62µm, Malvern’s Quality Audit Standard (QAS).
Lactose 'seeding' experiment
Four 20mg aliquots of lactose were weighed out. The powder was handled carefully to avoid compaction or adhesion to the weigh boat. One of the aliquots was run as a reference; 1mg of QAS glass beads was added to the others (Figure 1).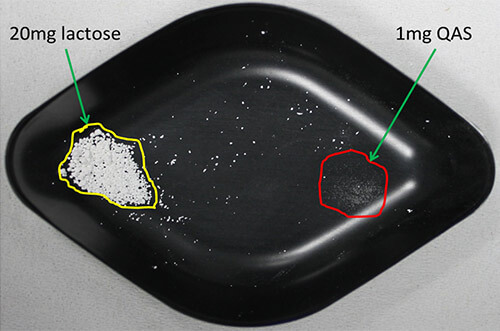
Figure 1: Weigh boat prepared with 20mg lactose and 1mg QAS glass beads. The particle size distribution obtained from a single 20mg aliquot of lactose is shown in figure 2A. The method used has been described elsewhere [1] and has a reproducibility of less than 1%RSD for Dv (50). In this case the Dv (50) is 4µm. Figure 2B shows the particle size distribution obtained from a single shot of QAS glass beads, where the Dv (50) is 62µm. The particle size distribution from the seeded sample, that is 20mg of lactose seeded with 1mg of QAS, is shown in figure 2C. The contribution from the QAS is clearly visible as a separate peak, with a mode of approximately 60µm.
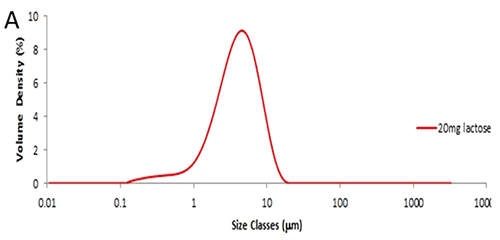
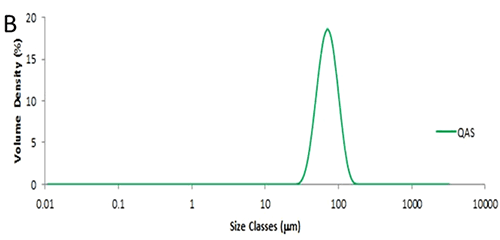
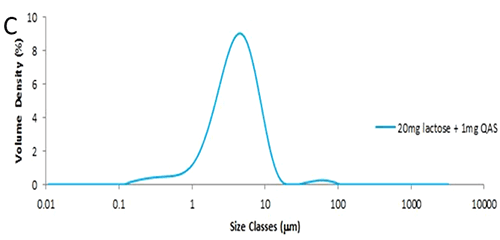
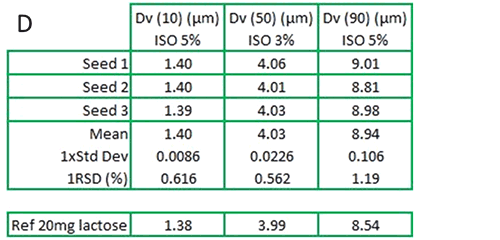
Figure 2: Particle size distributions obtained from A: 20mg of fine grade lactose; B: QAS glass beads; C: 20mg lactose seeded with 1mg QAS glass beads; D: Particle size statistics and measurement reproducibility based on three measurements. The percentiles have increased slightly due to the influence of the added QAS (figure 2D). While the QAS is present in a 1:20 ratio by mass, a simple calculation shows the number ratio will be of several orders of magnitude lower. Despite the presence of the QAS, the measurement remains highly reproducible with an RSD of just over 1% for Dv (90): the ISO standard for laser diffraction advises that the RSD for Dv (90) should be below 5% [2] for repeat measurements of the same sample.
Summary
Some industries, including pharmaceutical, have a requirement to measure small quantities of dry powders. Typically the powders are fine with a tightly controlled size distribution. However, it is useful to demonstrate that small numbers of oversized particles can be detected. This scenario was tested with the Aero S and Mastersizer 3000, by seeding a fine grade of lactose with glass beads, and this instrumental configuration was able to detect the “seeded” large particles easily and reproducibly.References
- Measuring small quantities of dry powder using the Aero S and Mastersizer 3000, Application note
- ISO 13320:2009 “Particle Size Analysis – Laser Diffraction Methods”.
Malvern provides the materials and biophysical characterization technology and expertise that enables scientists and engineers to investigate, understand and control the properties of dispersed systems. These systems range from proteins and polymers in solution, particle and nanoparticle suspensions and emulsions, through to sprays and aerosols, industrial bulk powders and high concentration slurries. Used at all stages of research, development and manufacturing, Malvern’s instruments provide critical information that helps accelerate research and product development, enhance and maintain product quality and optimize process efficiency. Our products reflect Malvern’s drive to exploit the latest technological innovations. They are used by both industry and academia, in sectors ranging from pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals to bulk chemicals, cement, plastics and polymers, energy and the environment. Malvern systems are used to measure particle size, particle shape, zeta potential, protein charge, molecular weight, mass, size and conformation, rheological properties and for chemical identification, advancing the understanding of dispersed systems across many different industries and applications. www.malvern.com Material relationships http://www.malvern.com/en/ [email protected]

