Determination of the common anions, such as bromide, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, nitrite, phosphate, and sulfate, is often needed in water analytics. Conventional colorimetric, electrometric and titrimetric methods are available for the determination of individual anions, but ion chromatography provides a single instrumental technique that may be used for rapid, sequential measurement. This Application Note presents the sensitive determination of anions in water samples using the isocratic AZURA Compact System with suppressed conductivity detection. Typically, anions can be rapidly and easily analyzed using conductivity detection with additional apparatus for the suppression of the eluent’s conductivity.

The stock standard solution was prepared by weighing in anion salt standards and dissolving them separately in deionized water. For the analysis of water, samples are often just filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter and injected to the IC system as also described in US EPA method 300.1 and the standard method 4110 (1, 2). More complex sample pretreatment is required if very low concentrations of anions have to be determined or if matrix constituents are interfering with the IC separation (3).
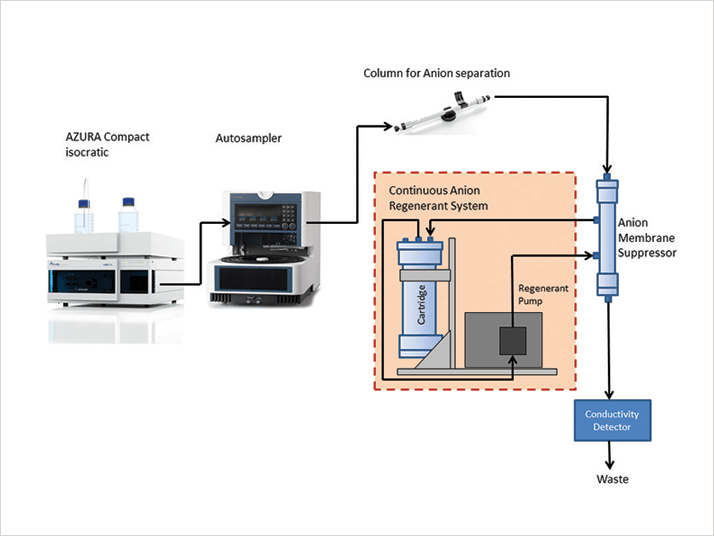
Column
Anion Column, 250 x 4 mm
Eluent A
4.5 mM Na2CO3, 1.4 mM NaHCO3
Gradient
Isocratic 100 % A
Flow rate
1.2 ml/min
Injection volume
50 µl
Column temperature
25 °C
SeQuant® SAMS™ robust suppressor for anion chromatography
SeQuant® CARS™ Continuous Regeneration System for SAMS™
The isocratic AZURA Compact system in combination with suppressed conductivity detection was found to be well suited for the analysis of anions in mixed standard solutions even in the low ppm region. Under the chosen conditions, the applied anion column separates all anions within 15 min as shown in Figure 2.
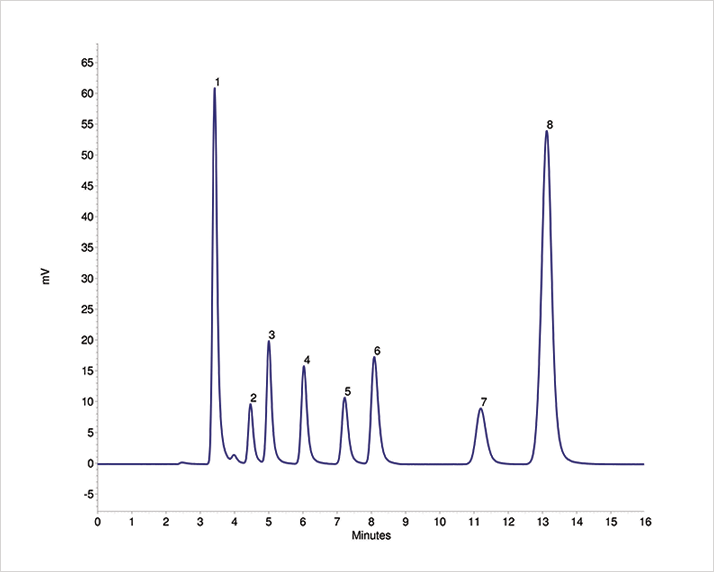
The column was designed specifically for compliance monitoring of inorganic anions in accordance with US EPA Method 300.0 (A) and 300.1 and low molecular weight organic acids. Common inorganic anions can easily be separated in a variety of sample matrices including drinking water, wastewater, process streams, and scrubber solutions with an optimized operating temperature of 30 °C to ensure reproducible retention times.
References
- John D. Pfaff, Daniel P. Hautman: US EPA method 300.1: Determination of Inorganic anions in drinking water by ion chromatography (Revision 1.0), National Exposure Research Laboratory Office of research and development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinatti, Ohio 45268 American Public Health Association: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, Standard Method 4110: Ion Chromatography with Chemical Suppression of Eluent Conductivity http://www.standardmethods.org/store/ProductView.cfm?ProductID=31 B. López-Ruiz, “Review: Advances in the determination of inorganic anions by ion chromatography”, Journal of Chromatography A, 881, 607–627 (2000). SeQuant: A practical guide to Ion Chromatography, ISBN 978-91-631-8056-9 (Sweden, 2007).





