Summary
In this technical note, we report the chiral separation of the most common 19 FMOC protected a-amino acids derivatives under reversed phase separation mode using Lux polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases. All FMOC a-amino acids analyzed in this study are baseline resolved with an analysis time below 25 min in isocratic conditions. The order of elution as well as the enantiomer identification are also reported.

Introduction
N-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMOC) a-amino acids are important building blocks for the solid phase synthesis of peptides.1 After the development of FMOC/tBu strategy2 for solid phase peptide syntheses, FMOC a-amino acids have become the raw materials of choice for the preparation of synthetic peptides. Using this methodology, long peptides (up to 100 residues) can be prepared in a few days with high yield from micro molar (g) up to molar scale (kg). As the number of amino acids residues creases, the final purity and overall yield of the peptide produced is directly affected by the chemical and chiral purity of the protected amino acids used. Currently, for the most common commercially available FMOC protected a-amino acids (19 natural amino acids), the expected enantiomeric purity is > 99.0 % enantiomeric excess (ee) for the L form and sometimes the purity required must be >= 99.8 % ee. This level of precision can only be achieved by very few analytical techniques, chiral HPLC being one of them. The main advantages of chiral HPLC analysis over other techniques are speed, detection level, and ease of use. HPLC is also used on a regular basis by the peptide chemists to analyze purified fractions as well as peptide purity. In this application, we report for the first time, the chiral separation of the most common commercially available FMOC protected a-amino acids under reversed phase conditions using polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases (CSPs) depicted in Figure 1.3
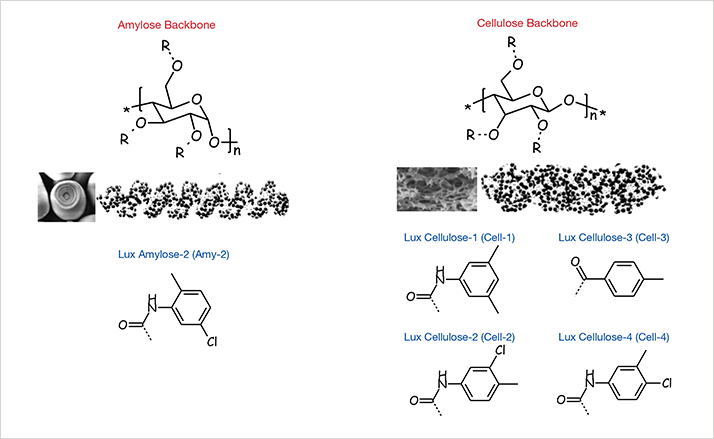 Figure 1. Structures of Polysaccharide-Based CSPs
Figure 1. Structures of Polysaccharide-Based CSPsAll analyses were performed using an Agilent® 1100 series LC system (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with quaternary pump, in-line degasser, multi-wavelength UV detector, and autosampler. Lux® columns used for analysis were obtained from Phenomenex (Torrance, CA, USA). The HPLC column dimensions were 250 x 4.6 mm ID and all columns were packed with 5 μm particles. FMOC protected L and D amino acids used in this study were provided by Bachem® (Bubendorf, Switzerland). All solvents were purchased from EMD (San Diego, CA, USA).





