Summary
Plastic tubing is available in a variety of opacities ranging from clear to translucent. The transparency of plastic tubing varies for reasons such as providing contrast for visual monitoring of fluid flow, decreasing exposure to ambient light, and making the tubing more distinct for machine vision technology. Visible-NIR transmission spectroscopy is used to assess the amount of frosting applied to plastic tubing to determine if the tubing meets the required opacity level.

Background
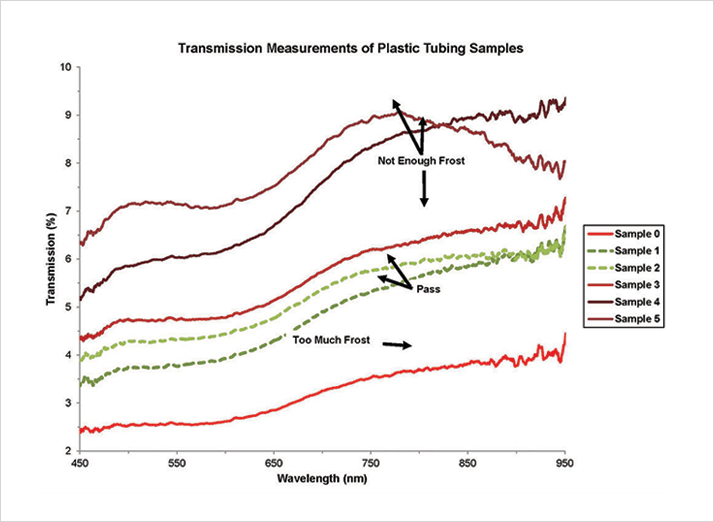
Plastic tubing is used everywhere – from the beverage dispenser at your favorite restaurant to the gas and liquid delivery lines in life-saving medical devices. In many applications that employ plastic tubing, visual contact with the flowing material is required to confirm flow and check for bubbles. Visual monitoring is facilitated by enhancing the contrast between the fluid and plastic tubing. Coatings, frosting and other surface modifications are used to vary the interaction of light with the tubing, making it easier to observe fluid flow. Modular spectroscopy components can be used to assemble a range of setups to measure the interaction of light with plastic tubing. In the case of frosted tubing, where light transmission must be kept within a narrow range to provide the desired tubing characteristics, Vis-NIR transmission measurements provide a straightforward method to assess frosting level.Measurement Conditions
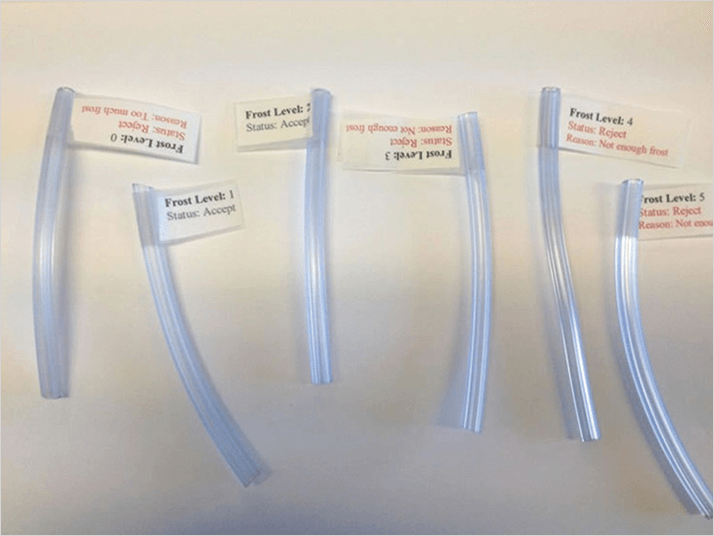
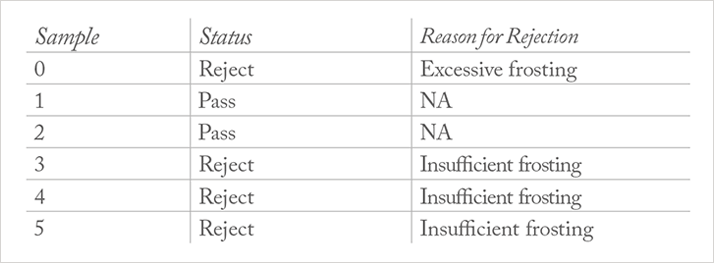
Samples of five plastic tubes with varying levels of frosting were used for the analysis (Figure 1). Details on the frosting level for each sample are provided in Table 1. Transmission measurements were made using an enhanced sensitivity Vis-NIR spectrometer. The tubes were placed between two collimating lenses in a transmission setup and adjusted until the most reproducible orientation was found.