Introduction
• Contaminations such as ions and organic traces present in ultrapure water affect LC-MS analyses and decrease perfomance of the analytical instumentation. The use of high purity solvents in LC-MS analyses is critical as it allows to avoid ghost peaks, high background, signal supression and formation of adducts.• Specifications for LC-MS grade bottled water vary from one manufacture to another. Standard tests for LC-MS system performance were adapted to demonstrate the suitability and the benifits of using fresh ultrapure water for LC-MS analyses.
• Ultrapure water quality can degrade significantly during storage. Flow injection analyses of stored ultrapure water show the effect of storage on ultrapure water quality.
• Laboratory environment can strongly degrade ultrapure water quality resulting in ghost peaks and noisy MS background. The benefits of obtaining freshly produced ultrapure water by discarding several liters prior to ultrapure water prior to collection are described. Ultrapure water from Merck Millipore water purification systems
• Fresh ultrapure water used in all the experiments was produced from a Milli-Q® water purification system fed by an Elix system. The Milli-Q® system was equipped with online resistivity and TOC monitors. Unless otherwise specified, a 0.22 μm membrane was used at the point-of-delivery purifier (Millipak)

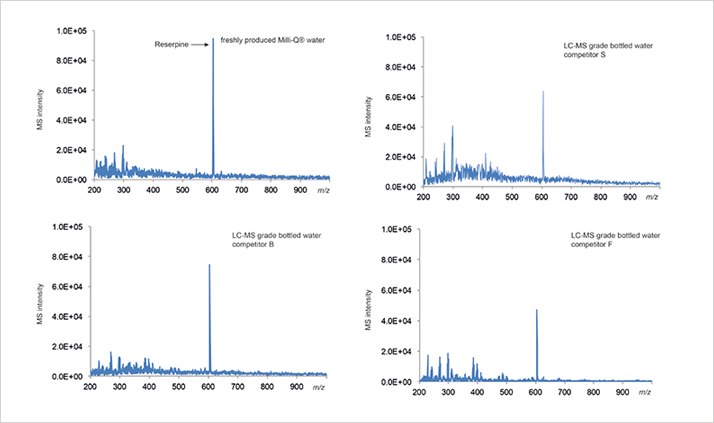
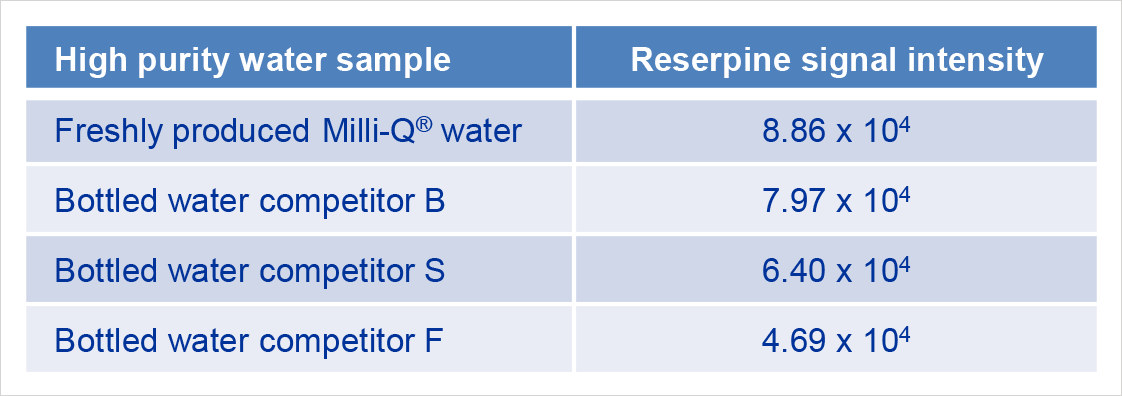
Reserpine test of different water samples
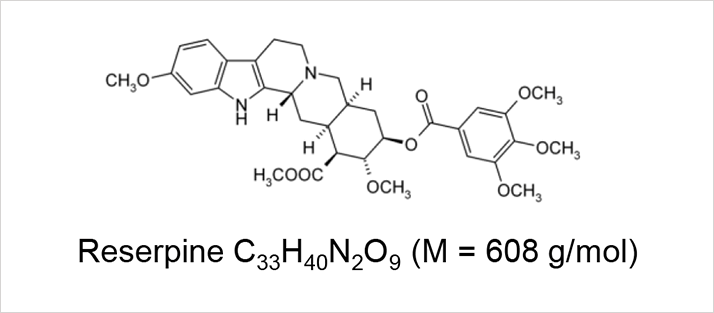
Suitability test using reserpine allows the evaluation of potential organic contaminants that can affect MS analyses especially when the analytes are in the high molecular weight range. Reserpine was dissolved in different high purity water samples to verify their suitability for LC-MS analyses.