Two fundamental requirements for obtaining accurate, and reproducible results in HPLC and UHPLC, are excellent peak shape and adequate resolution between the analytes. Good symmetrical peak shape in Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPLC) comes from an appropriate choice of column, mobile phase, and a variety of other parameters including sample solvent, injection volume, buffer type and strength. A high quality column made from ultra-pure, low-metal-content silica, can play a key role in minimising secondary interactions of acidic and basic analytes with the stationary phase, which can lead to tailing and fronting peaks. Combining a series of stable, unique bonding chemistries with ultra-pure, silica particles, can make the method development process faster, more comprehensive and more effective. Moreover, by choosing shorter column geometries with smaller particle sizes, such as 1,7; 2 and 3 μm particles, comprehensive method development and evaluation of the ‘chromatographic selectivity space’ for analytes can be accomplished faster.
The Resolution Equation and Selectivity, The Most Powerful Parameter
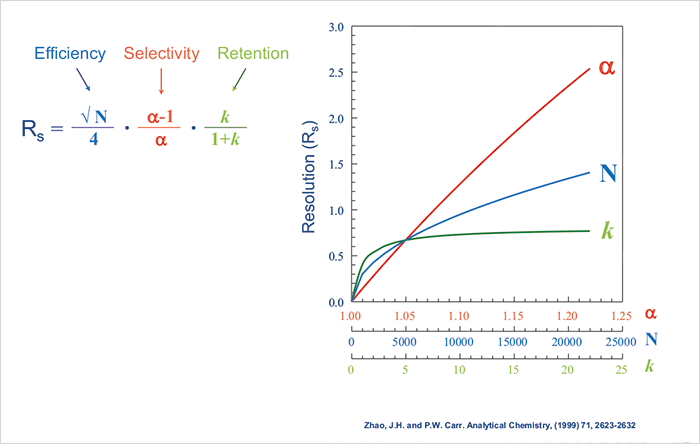
Well known forms of the resolution equation (Equation 1) describe the relationships between column efficiency (N), retention (k) and selectivity (α, or relative retention) and their effects on resolution between peak pairs. Representing this equation as a graph, it can be simply demonstrated that a change in selectivity has the most dramatic effect on analyte resolution (Figure 1).