With the increasing demand in product quality and safety assurance for antibiotics, sensitive analytical methods are required. HPLC with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) is the best analytical platform that fulfils all the criteria including sensitive impurity profiling, and the detection of by-products at low cost of operation and ownership (unlike LC/MS).
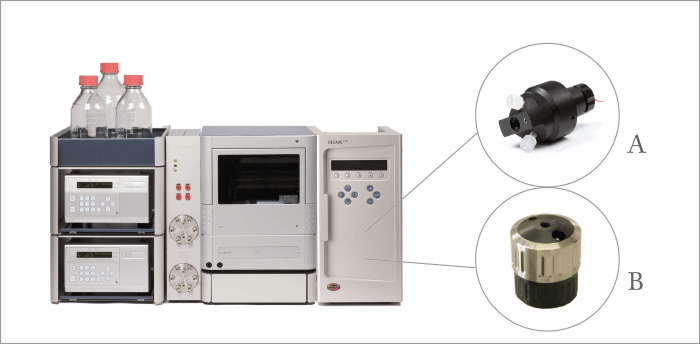
To guarantee ease of use and reliable results, Antec Scientific has developed a dedicated Antibiotics Analyzer that can be used for any type of aminoglycoside or macrolide antibiotics analysis.
ECD-PAD: the ideal detection
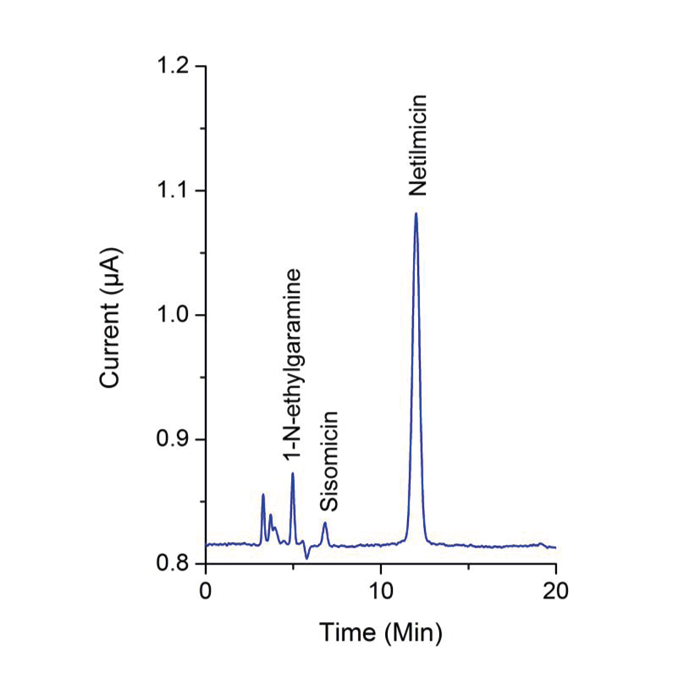
Both categories of antibiotics (aminoglycosides and macrolides), as well as most relevant impurities and by-products, contain one or more carbohydrate moieties on each molecule. This makes the use of pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) the ideal analytical technique, not only for the analysis of the antibiotic itself but in particular for the sensitive analysis of impurities and by-products. The preceding separation can be based either on reversed phase HPLC with post column addition of sodium hydroxide or the use of high performance anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC).
Two types of electrochemical flow cells are available: The FlexCell with easy exchangeable gold (Au) working electrode for routine use and the SenCell with integrated Au electrode and a stainless-steel auxiliary electrode, which is a requirement in some EP/USP monographs.