Abstract
PEGylation, the process by which polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains are attached to protein and peptide drugs is a common practice in the development of biopharmaceuticals to prolong serum half-life and improve pharmacokinetics of a drug. There is increasing demand for chromatographic methods to separate the modified isoforms from the native protein. This application note describes the use of size exclusion and ion exchange chromatography for the characterization of PEGylated lysozyme.

Introduction
Chemical modification of therapeutic proteins in order to enhance their biological activity is of increasing interest. One of the most frequently used protein modification method is the covalent attachment of poly (ethylene glycol) which is called PEGylation. This polymeric modification changes the biochemical and physicochemical properties of the protein, which decreases the in vivo clearance rate and reduces toxicity and immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins.After PEGylation the reaction mixture has to be purified in order to remove non-reacted protein and undesired reaction products. Chromatography as the most common purification method is influenced by PEGylation because of masking and shield effects of the covalently linked PEG molecule. Lysozyme is a well known standard protein, which is often used to determine the dynamic binding capacity of Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC) resins; therefore we decided to use PEG-lysozyme as a model protein in our study. PEGylated lysozyme was produced out of methoxy- PEG-aldehyde (with a MW of 5 kDa, 10 kDa and 30 kDa) and chicken egg white lysozyme in phosphate buffer in presence of sodium-cyano-borohydrid (NaCNBH3) as reducing agent. The PEGylation reaction takes place between the aldehyde group of methoxy-PEGaldehyde and free amino acid group (NH2-group) of lysine residues within the lysozyme (see Fig. 1).
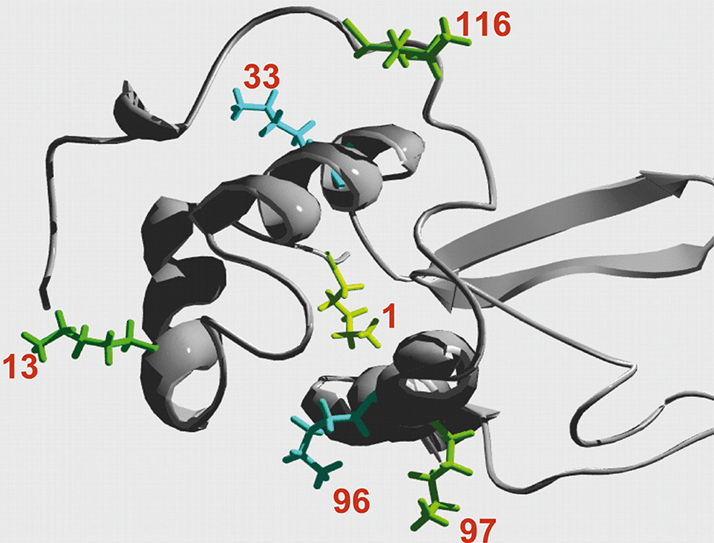 Figure 1. Lysozyme has six lysine residues as possible PEGylation reaction sides.
Figure 1. Lysozyme has six lysine residues as possible PEGylation reaction sides.The product mixture was analysed by a TSKgel G3000SWxl SEC HPLC-column, SDS-PAGE (not shown), IEC (TSKgel SP-5PW (20) and TSKgel SPNPR strong cation exchange (SCX)) and subsequent MALDI-TOF MS analysis (not shown).





