Summary
This technical brief aims to demonstrate the performance of GC-MS using hydrogen carrier gas. Here we compare the performance of hydrogen and helium for the analysis of a complex mixture. Results show that by using hydrogen, chromatographers can achieve superior results to helium, with faster run times and taller, sharper peaks.

Introduction
Owing to the worldwide shortage of Helium, many GC-MS users are now using hydrogen for carrier gas in their GC-MS analyses, however there are still fears about the safety of hydrogen and its reactivity with analytes. This study aims to show that hydrogen carrier gas produced by a hydrogen generator is suitable for GC-MS analyses and that use of hydrogen can give improved chromatographic results compared with helium as carrier gas.
Experimental
Reagent: 0.5 μL of a 76-compound mixture (Restek Megamix cat. No. 31850) in DCM.
MS:
Bruker SCION-SQ GC-MSD
MS source: 330 °C
Mass Range: m/z 45-500
2 min solvent delay, 120 ms scan time.
GC:
Column: BP-5MS column (20m x 0.18mm with 0.18 μm film thickness)
Oven: 45 °C (1 min hold) ramped at 30 °C/min to 310 °C (5 min. hold)
Injection: Pulsed-split injection (inlet temperature 290 °C , pressure 40 psi for 0.3 min, 70:1 split)
Carrier:
Peak Precision Generator Hydrogen, 1 mL/min
Results
The results of this technical brief show that by using hydrogen carrier gas, chromatographers can shorten run times compared with helium without compromising peak separation (Figure 1.). The results also show that hydrogen can improve not only run time efficiency, but signal strength and resolution.
Discussion
Hydrogen produced by a hydrogen generator is a safe and suitable alternative to helium for GC-MS carrier gas. With the installation of an in-oven hydrogen leak detector, along with the failsafe mechanisms in place within the generator, lab users can work safely with hydrogen.
EPA method 8270 allows for the use of both helium and hydrogen for carrier gas and results from the analysis of the complex mixture show that hydrogen can give superior separation of analytes despite operating at higher linear velocities. The lower viscosity and resulting higher efficiency of hydrogen compared with helium allows for the use of narrower bore columns, which gives chromatographers the opportunity to further improve separation.
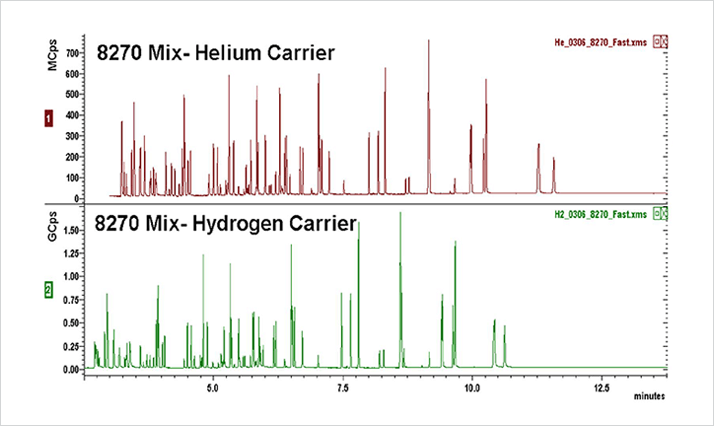 Figure 1. Results showing faster elution of compounds and greater peak height when using Hydrogen as a carrier gas.
Figure 1. Results showing faster elution of compounds and greater peak height when using Hydrogen as a carrier gas.




