Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA), figure 1, is a synthetical organic compound, a diphenylmethane derivative. BPA is frequently used in plastics and epoxy resin production, where final consumer products are clear and durable. BPA is used in polycarbonate, a high performance transparent, rigid plastic ( used for baby y and recycling water bottles). Another common use of epoxy resins containing BPA is surface coating of food and beverage cans. BPA can migrate in small amounts into food and beverages stored in materials containing the substance. Canada became the first country to declare BPA as a toxic substance in 2010. BPA is permitted in the European Union (EU) under Regulation 10/2011/EU for use in food contact materials, i.e. plastic materials and articles intending to come into contact with foodstuffs. However, the EU and the United States have banned BPA use in baby bottles. The reason is that Bisphenol A is thought to act as an endocrine disruptor and may lead to negative health effects.

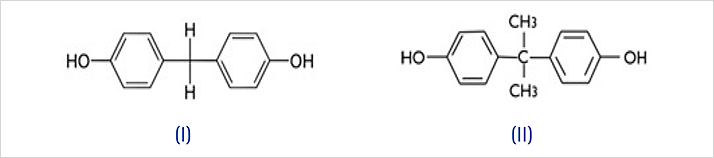 Figure 1. The chemical structure of Bisphenol F (I) and Bisphenol A (II).
Figure 1. The chemical structure of Bisphenol F (I) and Bisphenol A (II).This application note presents a rapid and inexpensive method for BPA screening in milk samples using a monolithic Chromolith® HighResolution RP-18 endcapped column and fluorescence detection on a Chromaster HPLC system. The method allows quantitative analysis of BPA above 1 ppb (1 ng/mL). The detection limit is sufficient and compare well with other reported non-MS based methods and can be used for BPA screening purposes. However, data from non-MS methods for BPA in food and beverage samples should be confirmed by MS methods; more specifically isotope dilution MS or tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) of regulatory reasons. The sensitivity of the method can be further improved by increasing lamp energy (from medium to high) but in order to maintain maximum detector Xenon-lamp lifetime this was unwanted. The analytical data presented herein demonstrate the excellent long term performance attained with Chromolith® columns.





