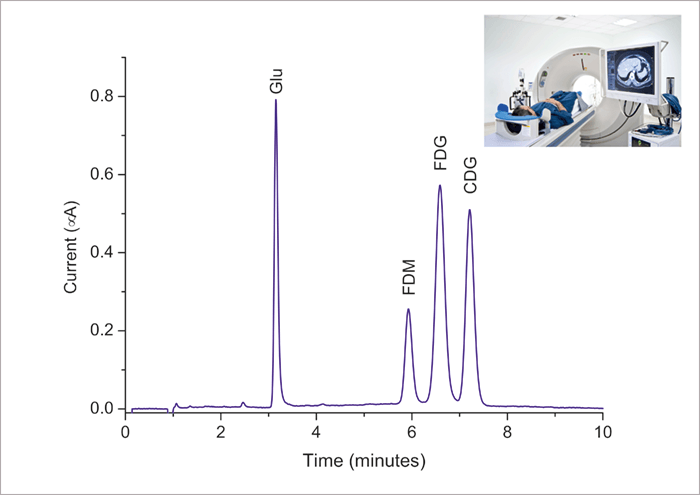
1. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer for PET scan imaging
In PET imaging, the radio-labelled tracer 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) can be used for the assessment of glucose metabolism in the heart, lungs, and the brain as well as for imaging tumors in oncology. The 109.8 minute half-life of 18F makes rapid and automated chemistry necessary; therefore [18F]FDG is produced in a cyclotron in close vicinity of the PET facility. Prior to injection of [18F]FDG into a patient, it is necessary to perform a purity check and determine the actual concentration of the unwanted by-products: 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-mannose (FDM) and 2-chloro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (CDG). HPLC-ECD is the industry standard for this important test due to its ability to selectively detect [18F]FDG, FDM and CDG at very low concentration levels. Compendial methods based on ECD are described in both the U.S Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP). These EP and USP methods are to a large extent similar and based on High Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography (HPAEC) in combination with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (PAD).