Introduction
Metabolomics and its toolset provide a foundation for quantitative biology and are indispensible for the detection of small molecules produced and/or transformed in the cells of living organisms.1,2 Different estimates indicate that a majority of differentially expressed analytes remain unknowns. The high sensitivity, peak capacity and reproducibility of GC-MS have made it one of the most widely used techniques for plant and animal metabolite profiling. Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) provides additional benefits such as reduced analysis times, effective peak deconvolution and an ability to interrogate rich data sets repeatedly for novel materials.

In addition, high resolution TOFMS instruments reduce matrix interferences and allow for production of high-quality, accurate mass data for robust formula determinations and library database comparisons. This application note demonstrates the value of both electron impact ionization (EI) and chemical ionization—high resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HR-CI) in identifying analytes in these complex metabolomic samples. These ionization techniques result in a more confident identification of metabolites through the complementary information. The labile nature of TMSderivatized metabolites and homologous nature of biological molecules make the need for molecular ion detection critical in metabolomics.
Results and Discussions
GC-MS compound identification in metabolomics relies primarily on retention indices and mass spectral library matching. In this study, the workflow included analysis by EI HR-CI to obtain a comprehensive profile for a mouse liver extract sample (Figure 1). Mass accuracies near 1 ppm for detected features resulted in robust elemental composition determinations for molecular, fragment, and adduct ions. Quality EI data facilitated searches against nominal mass libraries as evident by the similarity values for the representative set of compounds in mouse liver extract (Table 1). Similarity values for these trimethylsilyl derivatives ranged from 831 to 919 out of a possible score of 1000 in the absence of leveraging the mass accuracy.
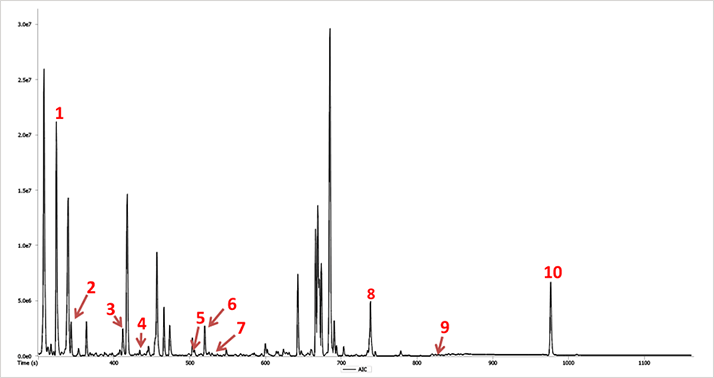 Figure 1. Analytical Ion Chromatogram (AIC) of Mouse Liver Extract (EI).
Figure 1. Analytical Ion Chromatogram (AIC) of Mouse Liver Extract (EI).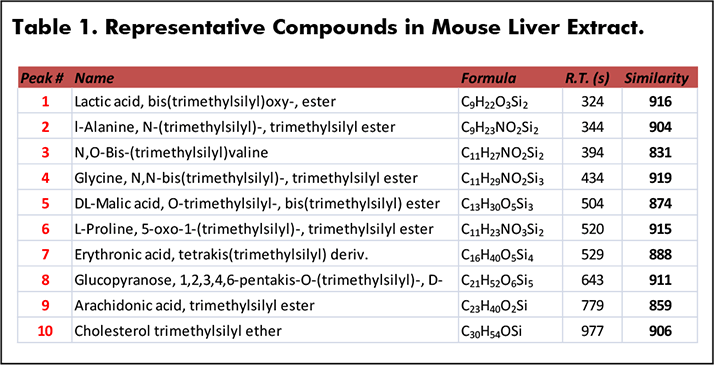 Table 1. Representative Compounds in Mouse Liver Extract.
Table 1. Representative Compounds in Mouse Liver Extract.Peak True (Deconvoluted) and NIST library spectra for two of the compounds, 5-oxo-proline and cholesterol, are shown below (Figures 2 and 3). The presence of molecular ions in these spectra make identification even more confident. Mass accuracy values for these TMS derivatives were 0.72 and -0.29 ppm respectively.
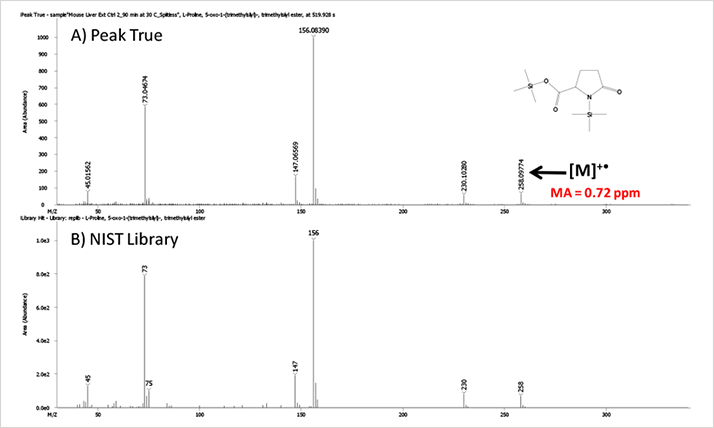 Figure 2. Peak True (A) and NIST library (B) Mass Spectra for the TMS Derivative of 5-oxo-Proline.
Figure 2. Peak True (A) and NIST library (B) Mass Spectra for the TMS Derivative of 5-oxo-Proline.




