Summary
A time-optimized method for the separation and determination of bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol F (BPF) using a KNAUER PLATINblue UHPLC system is presented in this application note. Reduction of analysis time to less than 1 minute is achieved by employing the BlueOrchid C18 stationary phase with a 1.8 μm particle size filled in a 2 mm ID column. A binary high pressure gradient configuration is used at a flow rate of 0.6 ml/min and detection is carried out with a photo diode array (PDA) detector.

Introduction
Bisphenols and especially BPA and BPF have become well known to the public in the last years due to their negative health effects. The concerns over BPA as the best known bisphenol began with baby bottles and spread to include other types of food and drink packaging. Bisphenols are used by the plastic producing industry as antioxidants for softeners, fungicides and as intermediates during the production process of polycarbonates, epoxides, phenol resins and dyes. European companies consume 1.15 Mio tons every year concerning to the EU. Most often BPA is used in the production of the two most commonly used polymers polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polycarbonate. In PVC production BPA acts as a polymerization inhibitor. After completed polymerization BPA residues may remain in the material. In polycarbonate production BPA is also an important monomer. Not all of the BPA is consumed in the production process and may leach out of the polymer later on. Today many applications of polycarbonate have been replaced with new copolymers such as co-polyester to eliminate BPA.1,2The different uses of bisphenols in the mentioned materials have in common that they are not bound tightly to the host material, which is problematic, because these materials are often used in products for the food industry, like cans, wrapping films and baby bottles. This way they find their way into the human body by leaching into food and drinks.1,2 Why is it important to determine bisphenols? BPA has shown to have similar effects like the hormone estrogen and can affect the human endocrine system. If the concentration in blood is high enough, humans react with disordered development of the sexual organs, the nervous system, and in behaviour. Especially before and shortly after birth the human body reacts particularly sensitive. That’s why bisphenols are controversially discussed by public authorities and scientists.2

The chemical structures of the most commonly used substances BPA and BPF which are determined in this work are shown in figure 1.
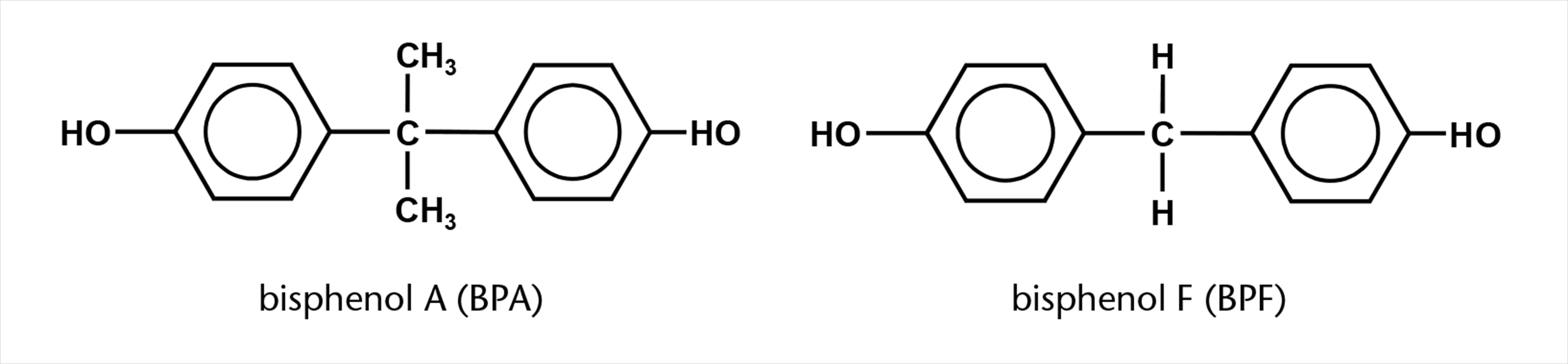 Figure 1: Chemical structures.
Figure 1: Chemical structures.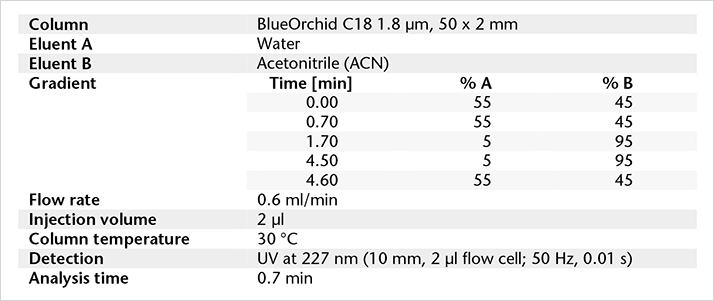 Method parameters.
Method parameters.Experimental: sample preparation
Bisphenols can be extracted from plastic products with high extraction ratios by using the solvent acetonitrile (ACN) at slightly elevated temperatures.3,4 A sample of 0.5 g of a wrapping film used for food packaging was cut into small pieces, 5 ml of ACN were added and the sample was put into a water bath at 40 °C for about 24 hours. After filtering through a 0.45 μm syringe filter, the sample was ready for analysis by UHPLC.
Experimental: preparation of standard solution
All standard solutions were prepared with water/ACN 50:50 (v/v). 10 mg of the two substances were dissolved in 10 ml water/ACN. After mixing and diluting to a concentration of 10 μg/ml and later on to 1 and 0.1 μg/ml for the calibration the standard solution was ready for analysis by UHPLC.





