Abstract
Therapeutic antibodies are enjoying high growth rates in the pharmaceutical market. In 2013, 7 of the top ten best-selling global drug brands were monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The main product characteristics to be analyzed in process monitoring and quality control are aggregation, fragmentation, glycosylation and charge heterogeneity. We present the fast analysis of mAb charge heterogeneity by cation exchange chromatography on TSKgel STAT columns.

Introduction
Charge isoforms of proteins result from deamidation of asparagine or glutamine residues or from incomplete removal of the C-terminal lysine residue. Besides isoelectric focusing, ion exchange chromatography is the method of choice to analyze charge heterogeneity of proteins. TSKgel STAT columns are packed with a non-porous polymer based stationary phase. Proprietary surface modification technology ensures a high density of charged groups. Compared to traditional porous IEX phases this yields outstanding resolution of charged species at shorter analysis time. TSKgel STAT columns are available as weak cation-exchanger (WCX, carboxymethyl) and strong cation exchanger (SCX, Sulfopropyl). Best performance is achieved when the columns are used with low dead volume chromatography systems such as modern UHPLC systems.
Results
The charge isoforms of two monoclonal antibodies were separated on a TSKgel CM-STAT weak cation exchange column and a TSKgel SP-STAT strong cation exchange column. Figure 1 shows the analysis of mAb A on both columns at pH 7. For this IgG the weak cation exchange column delivers a better separation of the basic variant from the main peak. As shown in Figure 2 this is not the case for mAb B, where the strong cation exchange column shows a better separation. Retention and resolution of the charged isoforms are dependent on the buffer pH as can be seen in Figure 3 for the analysis of mAb B on TSKgel SP-STAT.
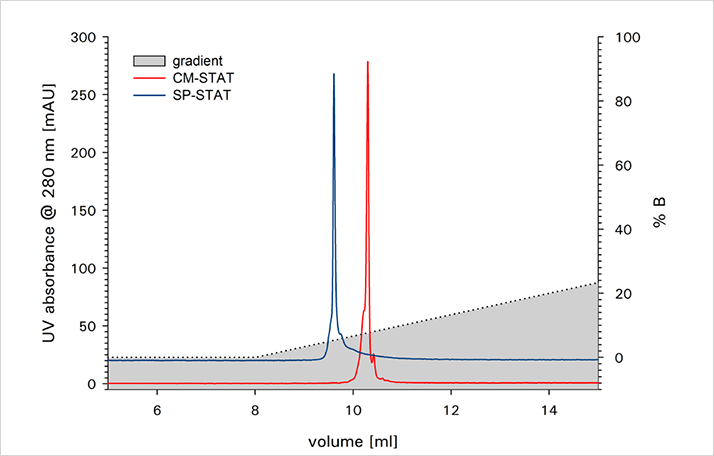 ANALYSIS OF mAbA ON WEAK AND STRONG ION EXCHANGE COLUMNS AT PH 7.0
ANALYSIS OF mAbA ON WEAK AND STRONG ION EXCHANGE COLUMNS AT PH 7.0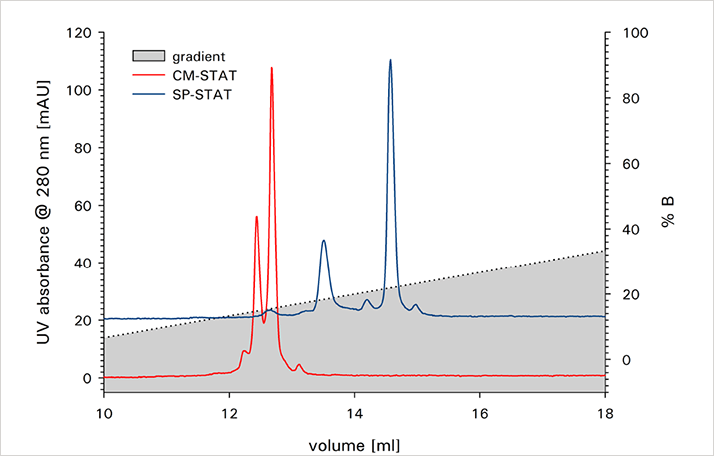 ANALYSIS OF mAbB ON WEAK AND STRONG ION EXCHANGE COLUMNS AT PH 7.0
ANALYSIS OF mAbB ON WEAK AND STRONG ION EXCHANGE COLUMNS AT PH 7.0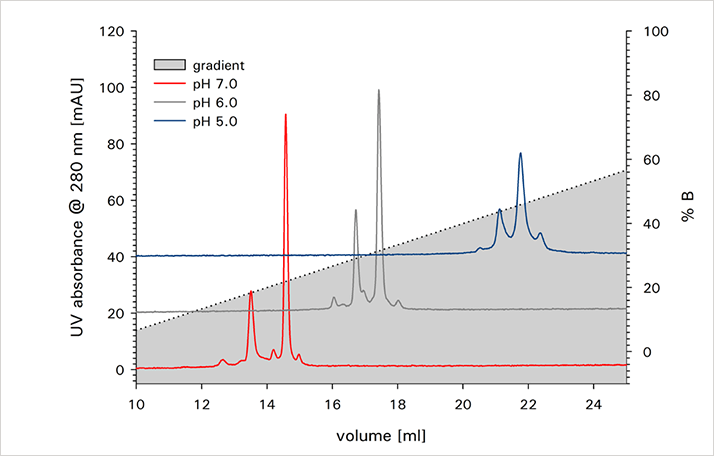 DEPENDENCE OF CATION EXCHANGE SEPARATION ON MOBILE PHASE PH
DEPENDENCE OF CATION EXCHANGE SEPARATION ON MOBILE PHASE PHMaterials & Methods
Columns: TSKgel SP-STAT (7 μm, 4.6 mm ID x 10 cm);
TSKgel CM-STAT (7 μm, 4.6 mm ID x 10 cm)
Mobile Phase A: 10 mMol/L sodium phosphate buffer
pH 7.0 (Figure 1, 2, 3)
10 mmol/L sodium phosphate buffer pH 6.0
(Figure 3)
10 mmol/L sodium acetate buffer pH 5.0
(Figure 3)
Mobile Phase B: 100 mMol/L phosphate pH 7.0 +
500 mmol/L NaCl (Figure 1, 2, 3)
100 mmol/L phosphate pH 6.0 +
500 mmol/L NaCl (Figure 3)
100 mmol/L acetate pH 5.0 +
500 mmol/L NaCl (Figure 3)
Gradient: 0 - 100 % B in 30 min
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection vol.: 10 μL
Detection: UV @ 280 nm
Sample: mAb A (2 g/L); mAb B (2 g/L)





