Introduction
The interest in comprehensive analysis of the metabolome has increased dramatically in the past decade. No single analytical technique can be used to accomplish this comprehensive study, but using various techniques in a complimentary way can make the task easier and enhance the chances of success. Gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is one of the techniques that are attractive to scientists involved in studies of the metabolome, due to the very good selectivity and sensitivity that it can provide. The only drawback was the lack of analysis speed. The addition of a Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer (TOFMS) with its high-speed capabilities overcame this difficulty. With acquisition speeds of up to 500 spectra/second, lack of spectral skewing, and unique Peak Find and Deconvolution algorithms, the LECO Pegasus GC-TOFMS facilitates the analysis of thousands of samples every year.

The objective of the study presented here is to develop a suite of toxicity markers from GC-TOFMS analysis, for use in pre-clinical screening of drug candidates. Isoniazid is a drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis and may induce severe hepatotoxicity in treated patients. Hydrazine is produced on exposure to isoniazid, and hydrazine levels can be correlated with the severity of the hepatocellular damage.
Pilot Study
A group of rats was dosed by gavage with the studied drug at two levels of concentration (100 and 300 mg/kg) for either one or 14 days. Urine samples from the animals were collected pre-dose at 0 to 6 and 6 to 24 hours following dosage. Aliquots of the urine samples were then extracted with methylene chloride and dried under nitrogen. Eight different solvents and solvent mixtures were tested for efficiency and reproducibility, and methylene chloride was selected based on the study results. Prior to injection into the GC-TOFMS system, the samples were derivatized with 40 μl of MSTFA +1% TMSD at room temperature for one hour, and diluted with 40 μl of hexane.
Experimental Conditions
GC:
Agilent 6890 GC
Primary Column:
Rtx-5, 10 m, 0.18 mm id, 0.18 μm film thickness
Oven Program:
50°C (0.2 minute hold) to 320°C at 20°C/minute
Inlet Temperature: 270°C
Injection Size:
1 μl with a split ratio of 5:1
Carrier Gas:
He at a constant flow of 1.5 ml/minute
MS: LECO Pegasus GC-TOFMS
Ionization: EI at 70eV
Mass Range (u): 45 to 600
Acquisition Rate: 20 spectra/second
Source Temp: 200ºC
Results
Figure 1 shows the total ion current (TIC) chromatogram for one of the samples analyzed. The total analysis time was 15.7 minutes, with the last peak of interest eluting in less than 14 minutes. 696 peaks were found automatically through data processing at a S/N ratio of 100. If the interest of the analyst is towards peaks of lower concentration, the S/N ratio can be decreased in order to increase the number of found peaks. Peak identification was performed using the NIST library. A more specialized library will most likely increase the number of identified peaks and improve the overall results.
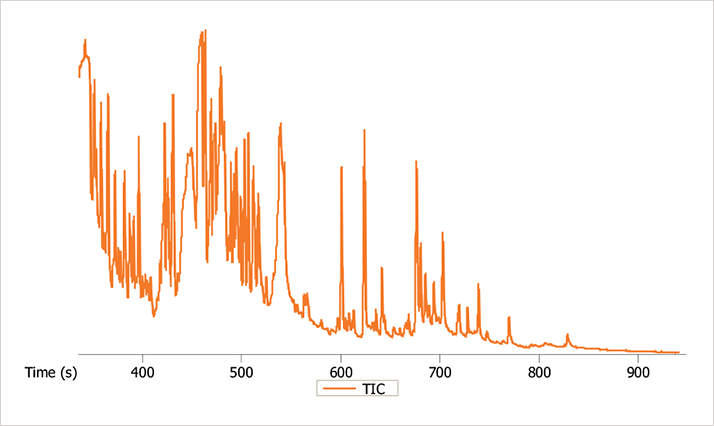 Figure 1. TIC chromatogram of one of the urine extract samples.
Figure 1. TIC chromatogram of one of the urine extract samples.




