Introduction
Glycosylation is one of the most common forms of post-translational modification of eukaryotic proteins. Glycosylated proteins (glycoproteins) make up the majority of human proteins. The polysaccharide side chains (Glycans) play critical roles in physiological and pathological reactions ranging from immunity to cell signaling, development and death. Besides the interest of researchers in characterizing gylcosylation pattern of glycoproteins for structure/function analysis, the thorough characterization of glycosylation is a major quality parameter in the production of biotherapeutics. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) is a well-recognized technique that effectively separates and quantifies isolated glycans

Hilic
HILIC is used primarily for the separation of polar and hydrophilic compounds. It is commonly believed that in HILIC the aqueous content of the mobile phase creates a water rich layer on the surface of the stationary phase based. This allows for partitioning of solutes between the more organic mobile phase and the aqueous layer. Hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions are supposed to be the dominating retention mechanisms in HILIC mode (Figure 1).
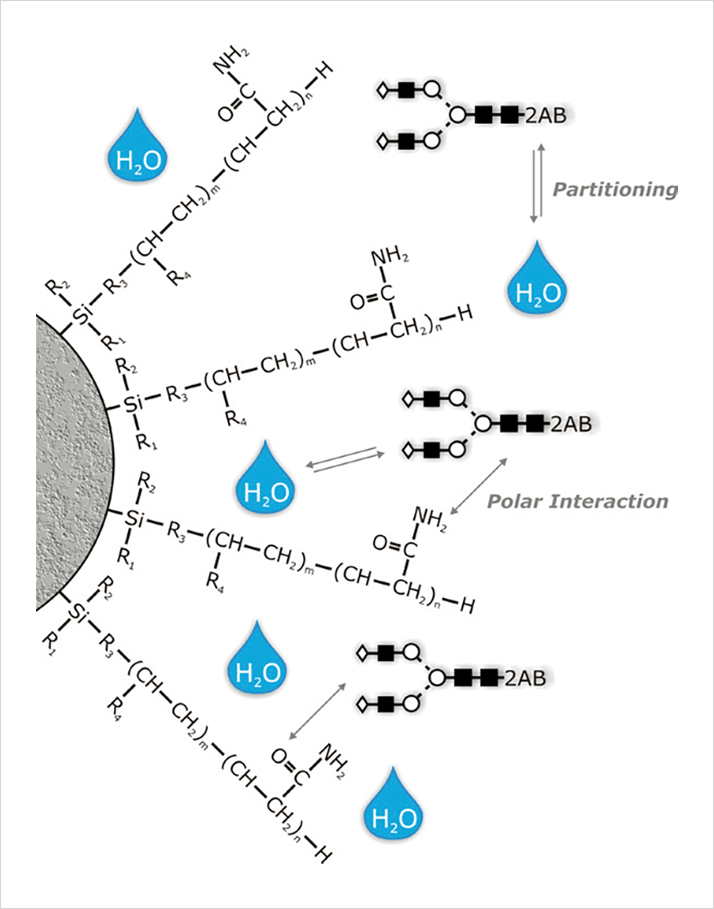 Figure 1
Figure 1Glycan Analysis
Glycoprotein analysis involves characterizing complex N- and O-linked structures composed of frequently similar and repeating sugar moieties. Several complementary analytical techniques are routinely used to characterize, identify, and quantify oligosaccharides isolated from glycoproteins. Besides mass spectrometric techniques, HILIC using amide-based stationary phases is a wellestablished, robust technique used by many laboratories to obtain high-resolution separation of N-linked glycans released from glycoproteins. Tagging the glycans with a fluorescent label such as 2-aminobenzamide (2AB) allows the sugars to be detected at femtomole levels.HILIC can separate structures with the same composition (isobaric glycoforms like α-2,3- or α-2,6- sialic acid) on the basis of both sequence and linkage. (1,2). TSKgel Amide-80 column chemistry is ideally suited for the separation of charged and neutral fractions of glycan pools in one run. The retention of fluorescence labelled (2-aminobenzamide, 2-AB) polysaccharides by TSKgel Amide-80 enables the identification of glycan structures by comparison to a labeled dextran ladder. The dextrane ladder is used to normalize retention times in order to calculate the number of glucose units (GU values) of the separated glycans. The GU values obtained after separation of sequential exoglygosidase digests can be used to predict the glycan structure by database query (Glycobase, autoGU).





