Introduction
Starches are polysaccharides produced by all green plants to store energy. They are the most important carbohydrates in the human diet, present in potatoes, wheat, maize (corn), and rice. Pure starch is a white powder insoluble in cold water. It consists of two types of molecules: the predominantly linear helical amylose (20-25%) and the lightly branched amylopectin (5-80%).

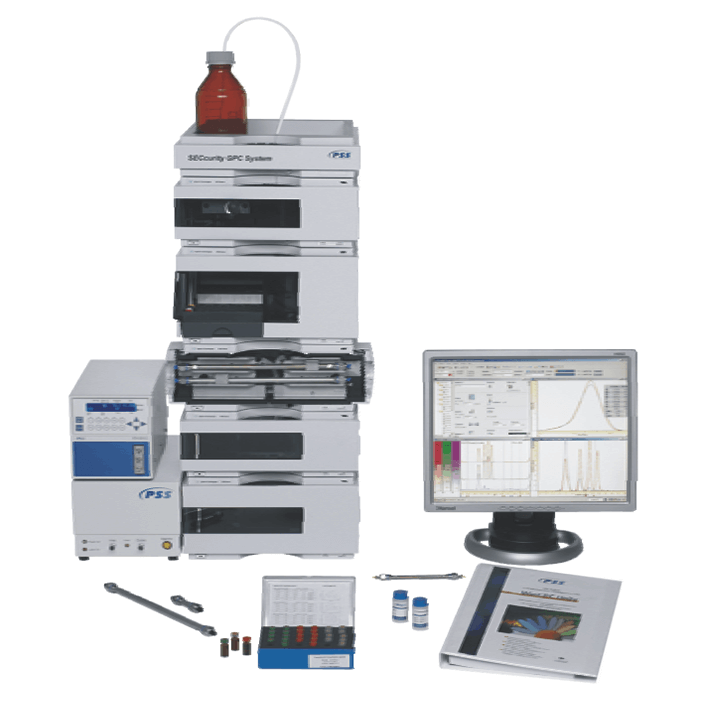
Experimental Conditions
Native waxy maize, tapioca, potato, and rice starch were wet-milled in order to determine the effect of milling on average molar mass (Mw) and molar mass distribution. 1 The molar mass distributions of the original pre-process and milled products were characterized by aqueous GPC/SEC with MALLS detection, using the following conditions: