Introduction
Hyaluronic acid is a polymer of disaccharides and can have up to 25,000 disaccharide repeat units. The molar mass range is from 5000 Da to 20 000 000 Da. Hyaluronic acid is mainly used in medical and cosmetic applications.
GPC/SEC is the method of choice for measuring the molar mass distribution of hyaluronic acid. True molar masses can be obtained when on-line multi angle light scattering is used in combination with a refractive index detector. The refractive index increment (dn/dc) for light scattering data evaluation can be determined on-line, offline using dedicated instrumentation or taken from literature.

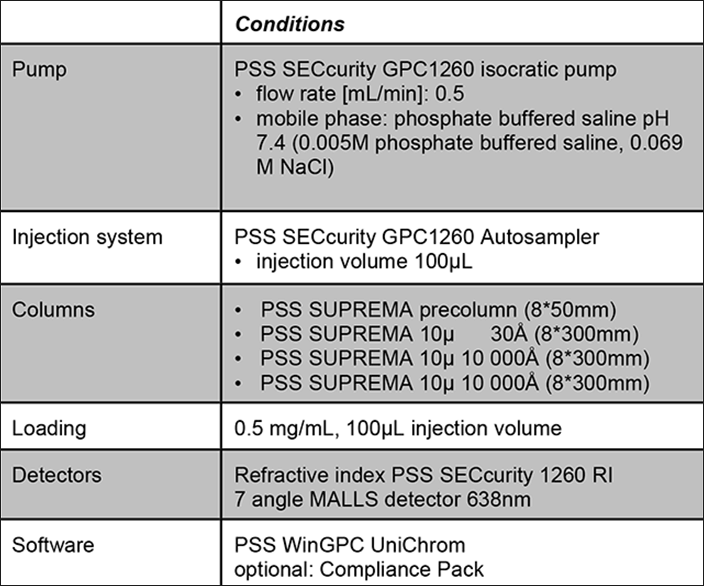
System Requirements
Procedure, Results & Discussion
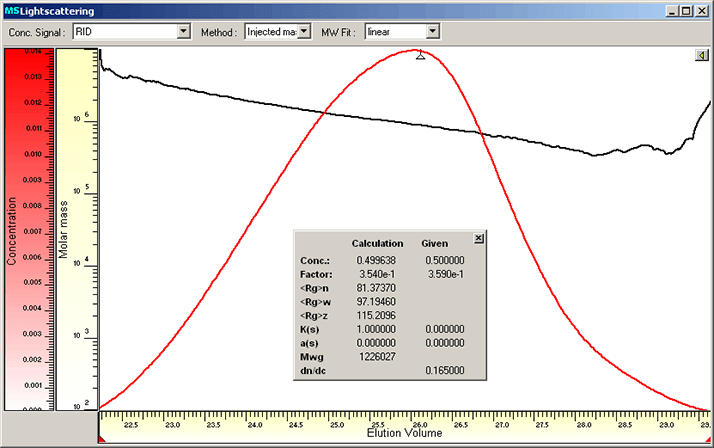
High molar mass samples require lower flow-rates and concentrations in GPC/SEC. The GPC/SEC conditions and columns have been optimized for high molar mass hyaluronic acid with respect to loading, flow-rate and column particle size and porosity. For sample preparation the water content of approx. 12 % has been taken into account. Due to the lack of high molar mass calibration standards the use of light scattering detection is recommended. This allows also to measure true molar masses. A refractive index increment (dn/dc) for hyaluronic acid of 0.165 has been used to evaluate the light scattering data.1 Figure 1 shows the slice concentration measured by the RI detector as well as the on-line measured molar mass. Sample recovery (compare Conc. Calculation vs. Given) was nearly 100% showing that all material eluted from the column.