Introduction
Isocyanates are both highly reactive and highly toxic low molar mass chemicals. One common technique used to take advantage of isocyanate reactivity while eliminating safety concerns is to synthesize polyurethane prepolymers for use in subsequent polymerizations. The physical properties of the resultant polymer are influenced to a large degree by the size of the polyol chains in the prepolymer. Harder polymers are formed with larger polyol chains and softer polymers are formed with smaller polyol chains.1 Here we report on the use of the EcoSEC GPC System to determine the molar mass and molar mass averages of an isocyanate modified polyurethane prepolymer (IMPP) with residual dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The low dead volume of the EcoSEC GPC System combined with the use of semimicro GPC columns allowed for an efficient separation and characterization of the prepolymer sample in less than 1 hour.

Experimental Conditions
Sample analysis was performed on a system consisting of an EcoSEC GPC System (HLC-8320) equipped with a refractive index detector (RI). Separation of unfiltered 20 μL injections occurred over a column bank consisting of two 6.0 mm ID × 15 cm, 3 μm particle size TSKgel® SuperH3000 (PN 17993) columns preceded by the appropriate guard column (PN 18002) (Tosoh Bioscience). The solvent and mobile phase were tetrahydrofuran (THF) (Fisher Chemical) at flow rates of 0.3 and 0.6 mL/min. Detector, pump oven, and column oven were maintained at 35 °C. For all chromatographic determinations, results are averages of three injections from two separate sample dispersions. Sample solutions were prepared by diluting 99% pure sample with THF for a final sample concentration of approximately 10 mg/mL. Samples were shaken manually for a minute and allowed to sit for 3 hours before analysis was performed. Data was processed with the EcoSEC GPC Workstation Software version 1.08. A RI calibration curve was created using PStQuick Kit-L polystyrene standards (PN 21915) (Tosoh Bioscience LLC) ranging in molar mass from 266 to 37,900 g/mol (Figure 1). Calibration curve data for both 0.3 and 0.6 mL/min were fitted with a cubic function and error values were no greater than 5%.
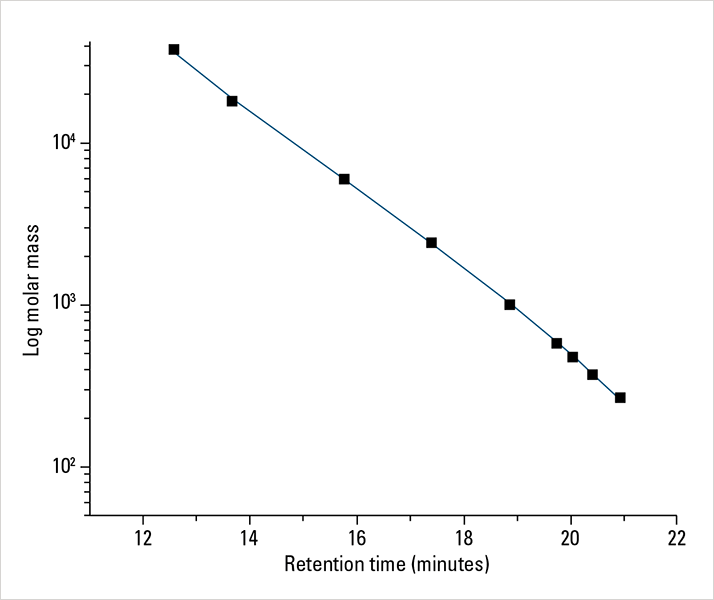 Figure 1. RI Calibrati on Curve for PStQuick Kit-L polystyrene sta ndards at 0.3 mL/min in THF at 35 °C
Figure 1. RI Calibrati on Curve for PStQuick Kit-L polystyrene sta ndards at 0.3 mL/min in THF at 35 °CResults and Discussion
An EcoSEC GPC System encompassing a refractive index detector was used to perform size exclusion chromatography analysis on an IMPP sample composed of 54% urethane prepolymer, 11.5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and 34.5% 1,1,1,3,3 pentafluoropropane. As seen in Figure 2, separation of the sample by size exclusion chromatography results in ten positive and two negative chromatographic peaks. The nine positive chromatographic peaks eluting from the column between 14.0 and 22.5 minutes correspond to the urethane prepolymer and 1,1,1,3,3 pentafluoropropane. Peaks 1 through 5 correspond to the urethane prepolymer and peaks 6 through 9 correspond to either the urethane prepolymer or 1,1,1,3,3 pentafluoropropane. The identities of peaks 6 through 9 were not confirmed due to the lack of availability of 1,1,1,3,3 pentafluoropropane.
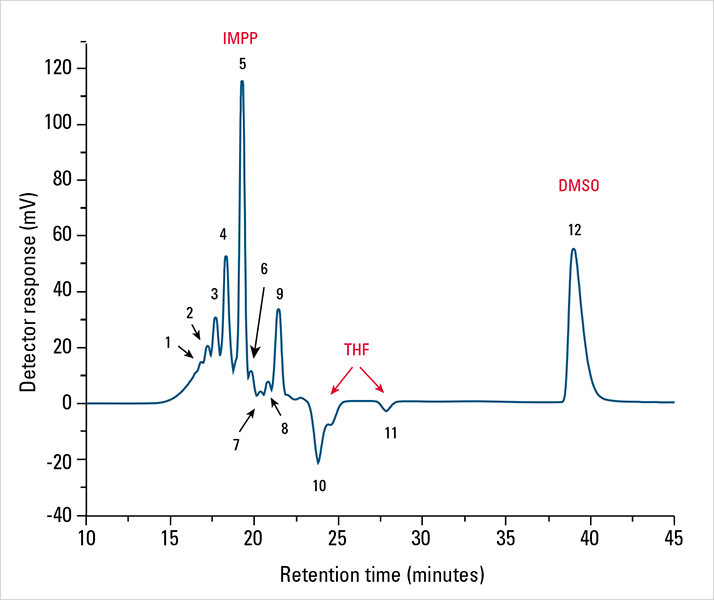 Figure 2. SEC elution profile of IMPP sample as monitored by RI (blue) at 0.3 mL/min in THF at 35 °C
Figure 2. SEC elution profile of IMPP sample as monitored by RI (blue) at 0.3 mL/min in THF at 35 °CThe two negative peaks at 23.7 and 27.8 minutes are indicative of the sample solvent, THF. Additionally, the latest eluting peak at 39.0 minutes is a result of residual DMSO present in the IMPP sample. Note that the DMSO peak elutes after the void volume of the column (~26.5 minutes) and as such is retained by a non-SEC retention mechanism.





