Introduction
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a 30400 dalton (Da) glycoprotein hormone that regulates the production of red blood cells (erythropoiesis). The glycosylation of EPO is highly variable because it contains multiple glycosylation sites, each of which can have a wide variety of glycan structures. This results in a huge complexity of glycan structures that is referred to as microheterogeneity.
Recombinant human EPO (rhEPO) has proven to be highly efficient in the treatment of different diseases such as anemias associated with cancer, chronic renal failure and HIV infection.

Detailed characterization of the glycan profile of biopharmaceuticals is a regulatory requirement as differences in glycosylation can affect both the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic behavior in the human body. Hence, it is necessary to develop advanced analytical technologies for efficient and detailed glycosylation analysis.
Results and Discussion
The method of choice for standard HPLC analysis of released glycans is typically hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) after labelling with 2-aminobenzamide (2AB) for sensitive fluorescence detection. Whereas HILIC efficiently separates glycans according to hydrodynamic radius, it is insufficient to fully resolve the complex mixture of branched glycan structures that are present in samples such as EPO. Fortunately, weak/strong anion exchange chromatography (WAX/SAX) provides a highly orthogonal separation that depends on the number and arrangement of acidic monosaccharides in the glycan. A combination of WAX/SAX and HILIC has a huge potential to enhance peak capacity in two-dimensional liquid chromatography (2D-LC) due to the highly orthogonal nature of these two separation techniques. The Agilent 1290 Infinity 2DLC solution enables online 2D-LC workflows for either comprehensive or (multiple) heart-cutting analysis. Comprehensive 2D-LC analysis, using two sample loops connected through a 2-position/-4-port duo valve, captures all peaks from the first dimension. If higher resolution is desired in the second dimension, the 1290 Infinity multiple heart-cutting 2D-LC solution provides more flexibility, for example, for applying longer cycle times or using longer columns.The 2D separation provides high peak capacity and resolution, and many of the co-eluting peaks from the HILIC dimension are well separated by WAX. The second dimension separation groups glycans by their charge. The neutral glycans, which elute immediately with the injection peak, are shortly followed by the singly charged glycans. More clearly separated, the double, triple, quadruple and a few quintuple (fetuin) charged glycans elute with increasing salt gradient in the second dimension. EPO isoforms are classified according to their net charge (epoetin alpha, beta, and so on). This setup enables simultaneous charge profiling in combination with a well resolved glycan peak pattern. The perfect orthogonality of both separation mechanisms is shown in the comprehensive 2D-LC chromatogram (Figure 1). This approach offers the possibility to screen and get an overview of the whole sample, which can be used for fingerprinting analysis.
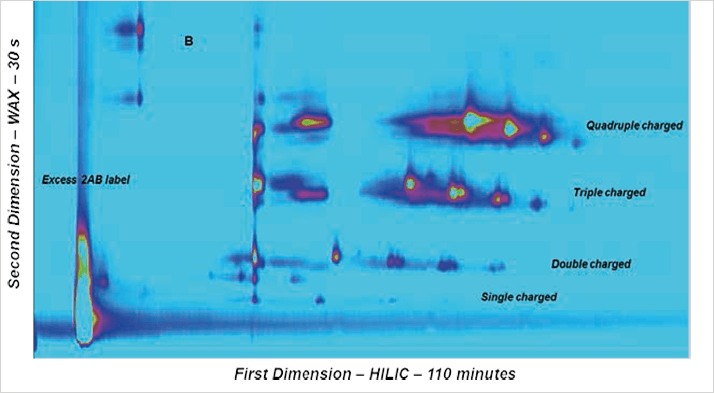 Figure 1. Comprehensive HILIC/WAX 2D-LC separation of fetuin (A) and EPO (B), showing highly orthogonal separation. The ion exchange chromatography in the second dimension reveals the charge pattern of the glycans.
Figure 1. Comprehensive HILIC/WAX 2D-LC separation of fetuin (A) and EPO (B), showing highly orthogonal separation. The ion exchange chromatography in the second dimension reveals the charge pattern of the glycans.




