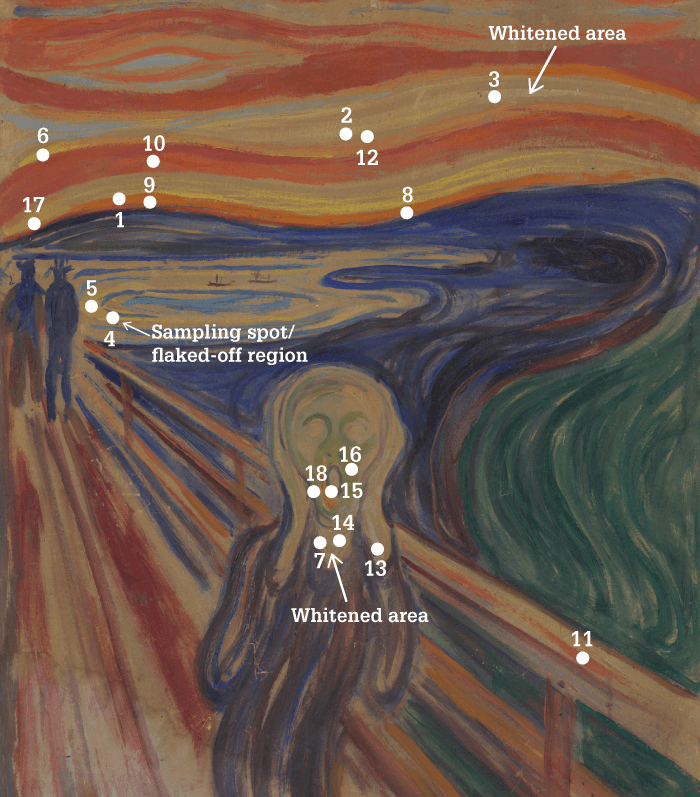
Edvard Munch’s “The Scream” has stood the test of time as a prominent portrayal of our anxiety-laden world, but the painting is beginning to show its age. In both the 1893 and 1910 versions of the painting, the yellow areas – where cadmium sulphide (CdS) paints were used – are degrading.
Why? A team of researchers at the National Research Council in Italy have shown – using non-invasive spectroscopy and synchrotron X-ray techniques – that moisture and mobile chlorine compounds are the major causes of this deterioration (1).
As well as analyzing the 1910 painting in situ at the Munch Museum in Oslo, the team took microsamples of flaking paint for analysis by micro X-ray diffraction, micro- X-ray fluorescence and micro X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy. By comparing the results to those obtained from their own artificially aged samples, the team demonstrated that CdS paint is converted to cadmium sulphate in high moisture conditions – even in the absence of light. To better preserve this masterpiece for future generations, the team suggests storing it in conditions with no higher than 45 percent relative humidity.
As many contemporaries of Munch also used cadmium-based paints, including Vincent van Gogh and Henri Matisse, the discovery could help improve conservation strategies across the art world.
References
- L Monico et al., Sci Adv. 2020 May; 6(20): eaay3514. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay3514




