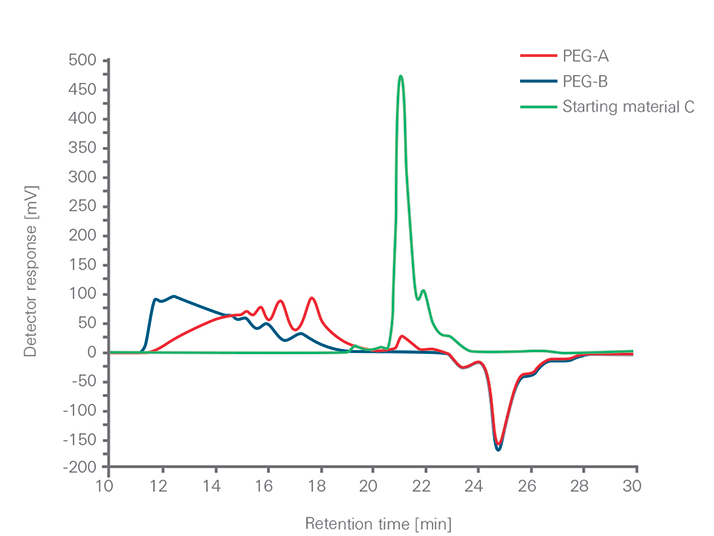
The utility of size exclusion chromatography (SEC or gel permeation chromatography, GPC) for synthesis monitoring and oligomeric analysis makes it an invaluable tool for characterizing synthetic polymeric material for use in medicine, as these materials require thorough characterization. The synthesis of two PEGylated synthetic polymers intended for use in medical applications was monitored and the oligomeric content was analyzed on an EcoSEC GPC System equipped with a column bank consisting of two 6.0 mm ID × 15 cm, 3 μm TSKgel® SuperH3000 columns. The synthesis process was analyzed by comparing the SECchromatograms of the two PEGylated polymers with that of one of the starting materials. From this comparison it was concluded that starting material remained in one of the PEGylated samples, PEG-A, and was absent in the other PEGylated sample, PEG-B (Figure 1). The SEC chromatograms of the PEGylated polymers also provided indication of differences in the molar mass distribution between the two PEGylated samples. Additionally, based on the peak-average molar masses Mp the oligomeric content of the two PEGylated polymers were shown to differ, with PEG-A containing mainly oligomeric species and PEG-B containing both low- and high-molar mass species.
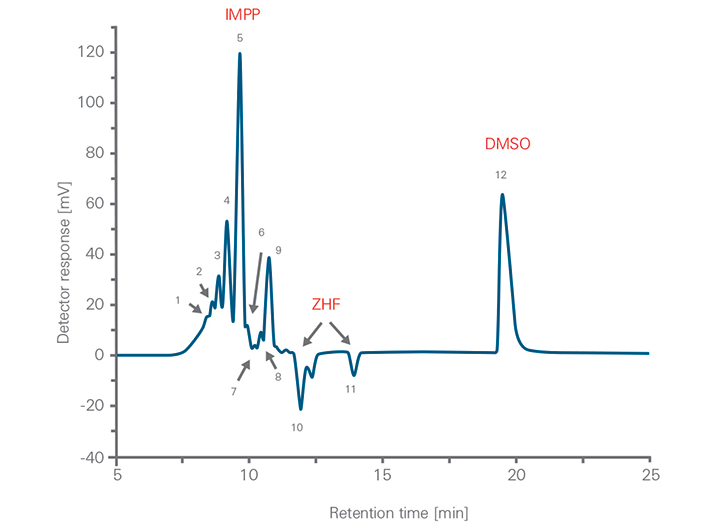
Isocyanates are both highly reactive and highly toxic low molar mass chemicals. One comon technique used to take advantage of isocyanate reactivity while eliminating safety concerns is to synthesize polyurethane prepolymers for use in subsequent polymerizations. The physical properties of the resultant polymer are influenced to a large degree by the size of the polyol chains in the prepolymer. Harder polymers are formed with larger polyol chains and softer polymers are formed with smaller polyol chains. The molar mass and molar mass averages of an isocyanate modified polyurethane prepolymer (IMPP) with residual dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were measured with an EcoSEC GPC System with a refractive index detector using a column bank consisting of two TSKgel SuperH3000 columns and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as mobile phase. The low dead volume of the EcoSEC GPC System combined with the use of semi-micro GPC columns allowed for an efficient separation and characterization of the prepolymer sample in less than hour. The molar mass averages and polydispersity index of the IMPP sample was determined using a polystyrene relative calibration curve. The chromatogram of the IMPP displayed twelve distinctive peaks. Peaks 1 through 5 were determined to be the urethane prepolymer component of the IMPP. The sample was analyzed at two different chromatographic flow rates, 0.3 and 0.6 mL/min. The flow rate of 0.6 mL/min (Figure 2) compared to that of 0.3 mL/min resulted in a decrease in analysis time from 45 minutes to 22 minutes.