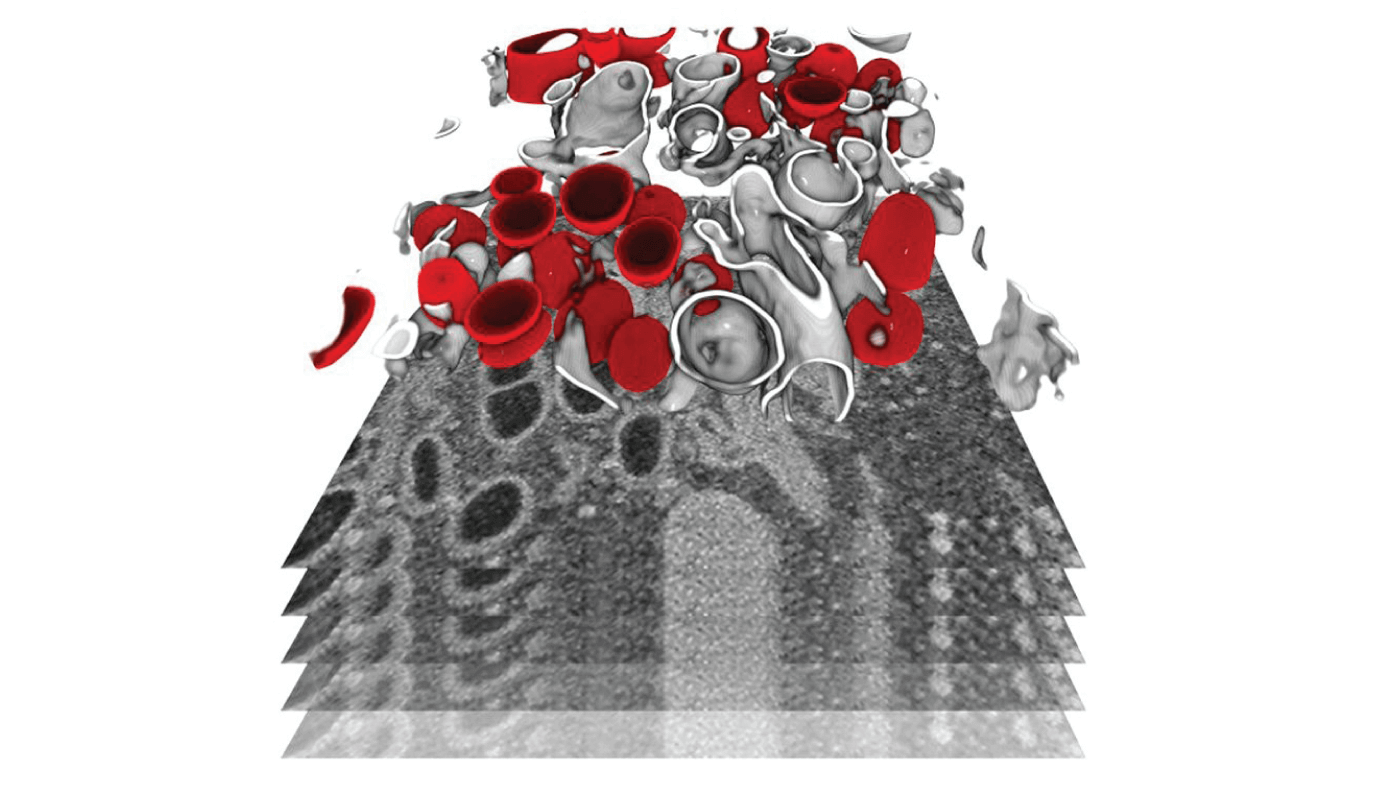
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, so too do global efforts to learn more about the virus. Researchers at Heidelberg University investigated how SARS-CoV-2 interacts with its host, replicates within the cell, and leads to cell death (1). They used focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy to image infected cells at the subcellular level in 3D – identifying structural changes caused by the virus.
They found significant remodeling of the endomembrane system of infected cells – a structure that defines different compartments within the cell. This change enables the virus to produce its own replication organelles, with the viral genome then replicating in large amounts in double-membrane vesicles (shown in red above).
References
- M Cortese et al., Cell Host Microbe, Online ahead of print (2020). PMID: 33245857.




