Introduction
Spidroins are a unique family of large, structural proteins that make up the bulk of spider silk fibers. The mechanical strength and elasticity of spider silk fibers have led to their successful use in the regeneration of peripheral nerves in rats [1]. Recombinant spider silk proteins have also shown potential for use in drug delivery systems [2]. Despite the wide range of medical applications that spider silk proteins offer, the production of these proteins on an industrial scale has only become possible fairly recently. The evolution of spidroins has been influenced strongly by a requirement for high tensile strength, a quality that does not necessarily guarantee conformational or chemical stability when other stresses are applied. This application note describes the use of a Zetasizer Nano ZSP to characterize the charge state of spidroins in different formulations. The earliest stages of spidroin aggregation in different formulations are then assessed using low-temperature synamic light scattering (DLS) thermal trend experiments.
Picture 1: Spider silk is well known for its extraordinary mechanical properties
Experimental
The zeta potential of spidroin samples was determined on a Zetasizer Nano ZSP using folded capillary cells. All electrophoretic light scattering (ELS) measurements were acquired using a fixed voltage of 75 V, or, given that the distance between the electrodes of a folded capillary cell is 6 cm, an electric field strength of 12.5 V/cm. A monomodal analysis model was applied, fast field reversal analysis being carried out alone on the samples in order to minimize the effect of joule heating. All ELS measurements were acquired at 25 °C after allowing for thermal equilibration of samples.
Samples were heated from 4 °C to 21 °C, with measurements acquired at temperature intervals of 1 °C. The system was purged with dry air during thermal trend experiments in order to minimize condensation on the cuvette wall.
Results
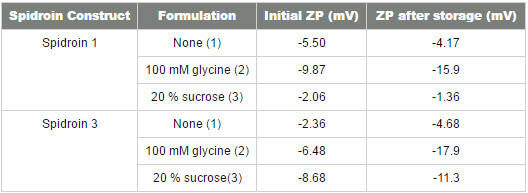
Table 1 shows the results of the cumulants analysis on two different spidroin protein samples. The data shown in table 1 indicates that the presence of glycine increases the zeta potential of both spidroins. The presence of sucrose, on the other hand, lowers the zeta potential of spidroin 1 and increases that of spidroin 3.
There is a large increase in the negativity of zeta potential measured during storage of both spidroins in glycine, suggesting large changes in the global charge arrangement of the proteins as a consequence of denaturation.
In order to assess the solution stability of the spidroin 1 formulations, thermal trend experiments were carried out. Data from these experiments are displayed in Figure 1, and indicate that the presence of sucrose increases the propensity of spidroin 1 to form large aggregates as the temperature is increased from 4 °C - 21 °C. The presence of glycine, on the other hand, clearly inhibits the formation of larger aggregates, the glycine formulation containing very few large aggregates at 4 °C, though there is some aggregate growth as the temperature is raised.
The aggregation-inhibition effect of glycine is consistent with the high zeta potential that this additive imparts on the spidroin, whilst the destabilizing effect expected fom the presence of sucrose is consistent with the lower zeta potential of the protein measured in the sucrose formulation.
Conclusion
Measurement of zeta potential using the Zetasizer Nano ZSP allows prediction of the aggregation propensity of protein in solution. Peltier temperature control allows DLS-assessment to be carried out at different temperatures, allowing the temperature of aggregation onset to be calculated, giving a direct measure of stability. Whilst most protein aggregation studies are carried out over a higher and wider temperature range than that used here (Zetasizers allow accurate temperature control from 0 °C - 90 °C), the high sensitivity of DLS to larger particles allows the earliest stages of aggregation to be characterized at relatively low temperatures.
>> Free download of the full Application Note as PDF
Malvern provides the materials and biophysical characterization technology and expertise that enables scientists and engineers to investigate, understand and control the properties of dispersed systems. These systems range from proteins and polymers in solution, particle and nanoparticle suspensions and emulsions, through to sprays and aerosols, industrial bulk powders and high concentration slurries. Used at all stages of research, development and manufacturing, Malvern’s instruments provide critical information that helps accelerate research and product development, enhance and maintain product quality and optimize process efficiency. Our products reflect Malvern’s drive to exploit the latest technological innovations. They are used by both industry and academia, in sectors ranging from pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals to bulk chemicals, cement, plastics and polymers, energy and the environment. Malvern systems are used to measure particle size, particle shape, zeta potential, protein charge, molecular weight, mass, size and conformation, rheological properties and for chemical identification, advancing the understanding of dispersed systems across many different industries and applications. www.malvern.com Material relationships http://www.malvern.com/en/ portal@malvern.com

References
- Allmeling, C., Jokuszies, A., Reimers, K., Kall, S., Choi, C. Y., Brandes, G., Kasper, C., Scheper, T., Guggenheim, M. & Vogt, P. M. (2008) Spider silk fibres in artificial nerve constructs promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Cell Proliferation, 41, 408-420 Hofer, M., Winter, G. & Myschik, J. (2012) Recombinant spider silk particles for controlled delivery of protein drugs. Biomaterials. 33, 1554-1562





