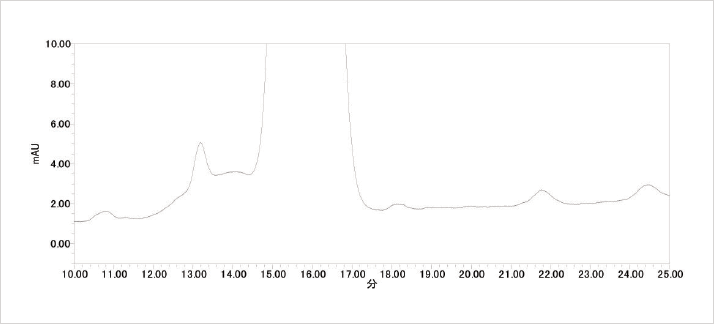
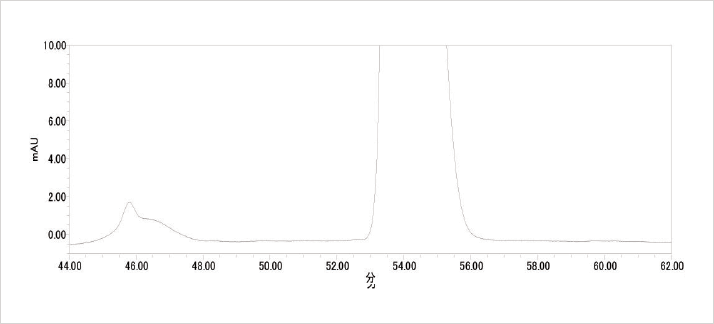
Synthetic impurities as well as degradation products are becoming increasingly important in today’s analytical laboratories. Over the past few years there have been steps made by The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) to produce a consensus guideline on the assessment and control of DNA reactive (mutagenic) impurities in pharmaceuticals to limit potential carcinogenic risk. In this current M7 step 2 draft document lower thresholds of impurities are mentioned. It therefore appears that there will be a need in the near future for HPLC with improved sensitivity and resolution.

Eluent: 20 mmol/L Phosphate Buffer/CH3CN/CH3OH = 45/40/15 (pre-mixed)
Wavelength: 210 nm
Column Type: LaChromUltra II C18
Max Pressure: 1350 bar (Coupled columns) Sample: Erythromaycin A: Wako pure chemicals
056-07361 DCH57893