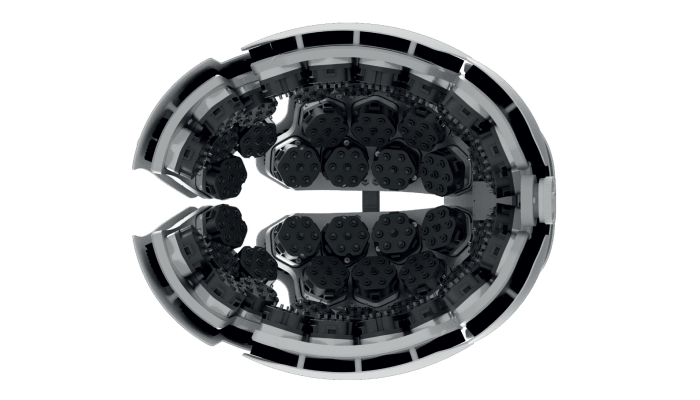
Although time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy (TD-fNIRS) is currently considered the pinnacle of non-invasive optical brain imaging techniques, it can be complex, cumbersome, and costly, and, therefore, is not yet widely employed in the field. Sensing a gap in the market, engineers from Kernel, a US neurotechnology company, designed a wearable brain-imaging device called Kernel Flow (1). Weighing in at 2.05 kg, the TD-fNIRS headset contains 52 modules arranged in eight plates that fit on either side of the head. Using picosecond laser pulses and detectors to estimate photon scattering and absorption in tissues, Kernel Flow measures changes in blood oxygenation that correlate with groups of neurons firing.
When developing Kernel Flow, the engineers evaluated other non-invasive brain imaging techniques, including EEG, ultrasound, fMRI and MEG, but ultimately homed in on TD-fNIRS - “the perfect combination of scalability, temporal resolution, spatial resolution, and wearability to build a mainstream brain interface,” according to Ryan Field, Kernel’s chief technology officer. [LR2] Importantly, the team wanted to overcome the limitations of traditional TD-fNIRS, while maintaining the performance of a research grade system. “Our goal was to build a scalable brain interface that could someday be used by anyone and everyone, and to create the infrastructure to enable the mainstream adoption of brain measurement,” says Field.
The team used standardized methods of assessment for brain imaging instruments and a commonly used validation task to assess the system’s performance; the results showed that the Kernel Flow headset demonstrated performance comparable to existing TD-fNIRS benchtop systems. Although these results are very promising, Kernel highlights the need for future work, including the collection of additional human neuroscience data and the evaluation of system performance with different hair and skin types. Both are things the team at Kernel is currently working on.
Kernel has expressed interest in applying their system to novel drug discovery, pain measurement and management, healthy brain aging, cognitive changes, and elite performance. “We believe that a large amount of high-quality data collected in a standardized way will be the key driver of innovation in applying brain measurements to personal insights,” explains Field. “We also hope that, one day, using a brain interface will become as common as picking up your phone.”
References
- Ban et al., Journal of Biomedical Optics (2022). DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.7.074710




