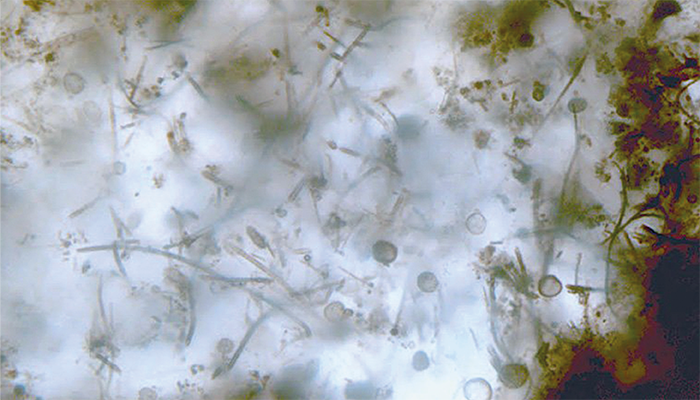
Image Credit: Tohoku University
A new imaging technique has unveiled key bioessential elements, such as phosphorus and molybdenum, in 1.9-billion-year-old microfossils from the Gunflint Formation in Canada. The findings provide the first clear evidence from geological samples that life, by this time, used phosphorus in cell membranes similar to modern life forms. Their approach combines optical microscopy, electron microscopy, and high-resolution secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) on a specially coated indium tin oxide (ITO) glass slide. By doing so, researchers were able to obtain clear images of ancient microbial life, revealing crucial metabolic clues.
"The detection of phosphorus has long been a challenge in microfossil research," notes Kohei Sasaki, co-author and researcher at the University of Tokyo, Japan. The technique's ability to distinguish trace elements from geological backgrounds could reshape our understanding of ancient metabolic processes, including how early microbes metabolized these important elements.
Read more here – and stay tuned for part two!
Study evaluating the use of LDI-TOF-MS for identifying metal elements in rice, finds that preparing rice as a tablet and using visible laser radiation provides optimal results. Link
Immune-related proteins and metabolites are upregulated, while osteopontin and CD44 levels decrease in a sex-dependent manner, correlating negatively with training load in short-track speed skaters, suggests research combining proteomics and metabolomics. Link
Mylène Soudani and colleagues optimize QuEChERS extraction method and LC-MS/MS and reveal significant PFAS contamination in freshwater fish from Swiss lakes – with many species exceeding EU safety limits. Link
Scientists develop a new method for determining calcium isotopes using ICP-MS/MS, overcoming interference from 40Ar by using ozone as a reaction gas to form CaO3+ and allowing high-sensitivity detection of less abundant isotopes like 43Ca. Link
Halide adducts with collision-induced dissociation (CID) tandem MS for direct differentiation of oligosaccharide isomers could have potential for diagnostic applications and characterizing synthetic oligosaccharides. Link

What does philosophy have to do with mass spectrometry and metabolomics?
For Gary Patti, science and philosophy aren’t separate disciplines but rather different approaches to understanding the world.
“Science requires two levels of inquiry: one is detail-oriented and evidence-based – you perform experiments and gather data. But if you’re a good scientist, you don’t operate just at that level. You have to consider a range of experiments to find patterns and draw higher-level conclusions. In many ways, that’s philosophy,” he says.
His philosophical interests have shaped his work in metabolomics – driving him to question conventional assumptions and explore the deeper implications of biological processes.
“I think the field of omics is quite philosophical because it involves abstract thinking – what is a metabolite? How big is an ‘ome’? Does the ‘dark metabolome’ really exist?” (Scroll down to Community Corner for more on that tricky question!)
You can read the full Sitting Down With interview here.
If you’re still wondering whether the “dark metabolome” is a figment of our imagination or not, earlier this year, Martin Giera and Gary Siuzdak, joined forces to examine the phenomenon of the “dark metabolome” – suggesting that in-source fragmentation accounts for over 70 percent of the peaks observed in typical LC-MS/MS metabolomic datasets.
We reached out to Martin and Gary to discuss their research: “Our study highlights the necessity for more selective data interpretation, ensuring that only real molecules are considered. This shift will enhance the accuracy of metabolic networks, avoiding distortions from non-existent molecules and providing a clearer, more reliable map of metabolic interactions.”




