Key challenges of isoprostane biomarker assays
- Lack of sensitivity – Quantification is poorly reproducible at low picogram levels in complex biological matrices.
- Overlapping interferences – Assay selectivity is hampered by interfering, co-eluting peaks.
- Multicomponent analysis in single assay –Single isomer measurement is a poor indicator of oxidative stress due to rapid degradation and variable isomer formation.
- Substandard data quality – Precision and accuracy are compromised at very low biomarker levels, giving results below accepted bioanalytical standards.

Key benefits of MRMHR for quantifying isoprostanes
- Maximized sensitivity – LLOQ of 5 pg/mL was an ~10-fold improvement over the triple quad MRM method.
- Increased selectivity and specificity – Reduced background noise enhances S/N ratios and reproducibility.
- Wider dynamic range – Measurements (5–10,000 pg/mL) are linear over 4-orders of magnitude (r = 0.9994).
- All-inclusive assay in one injection – Both known and unknown oxidative stress markers can be monitored simultaneously with a high-resolutionTOF-MS scan.

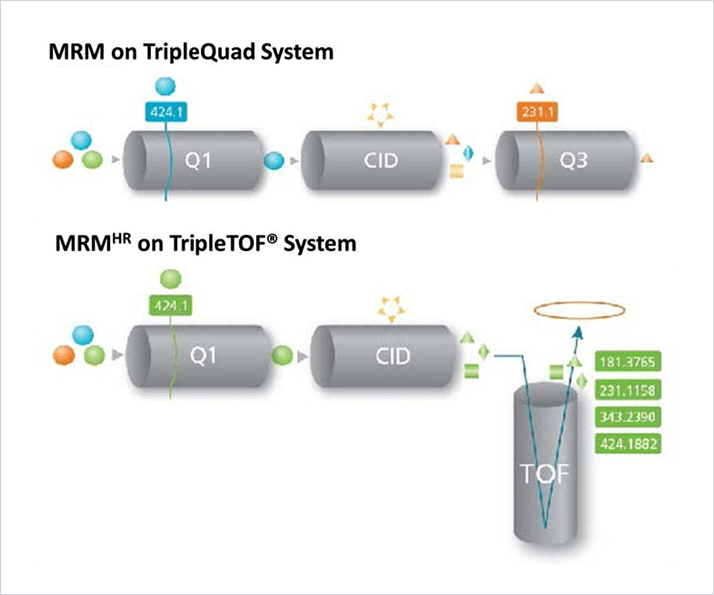 Figure 1. Schematic overview of MRMHR acquisition technique on a TripleTOF® System compared to standard triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Figure 1. Schematic overview of MRMHR acquisition technique on a TripleTOF® System compared to standard triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.Key features of the MRMHR workflow on the TripleTOF® System
- MRM-like quantitation – High-specificity is obtained using a narrow extraction width to mine high resolution TOF data.
- Simultaneous, multicomponent analysis – Fast acquisition rates can collect full-scan, MS/MS spectra for multiple precursors without additional cycle time.
- Fast cycle times maintained – Processing speed allows for sufficient peak coverage, even with fast LC separations.





