Introduction
Monoclonal antibodies (mAB) are increasingly growing in importance for the diagnosis and therapy of various diseases, including cancer as well as autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
One essential parameter to define their quality of is the content of aggregates (dimers, trimers and higher aggregates). These aggregates can be formed during processing and purification or are the result of long-term storage. Due to the aggregation antibodies lose their pharmaceutical efficacy and can facilitate immunology response.
Antibody fragments, which lack the Fc region, can be used for the treatment of diseases. Also they can be the result of degradation of full length antibodies. Therefore a GPC/SEC method which offers the opportunity to analyze antibodies and their aggregates as well as antibody fragments simultaneous with superior resolution is worthwhile, as well as a highly sensitive detection such as light scattering detection.

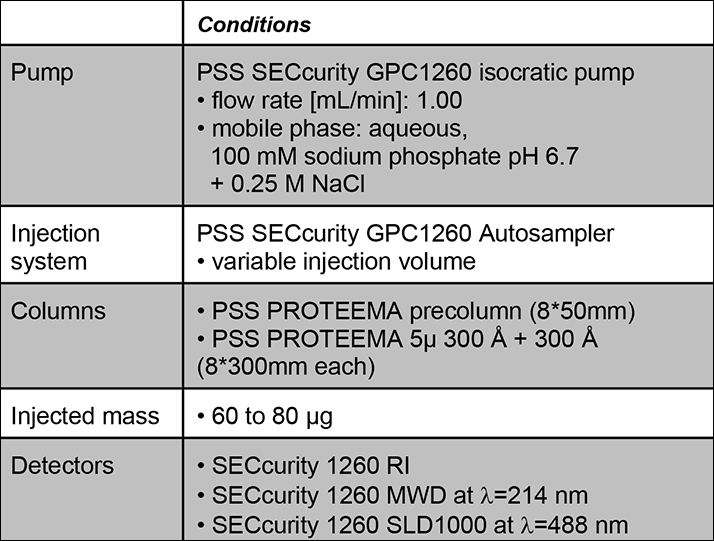
Procedure, Results & Discussion
A multidetection GPC/SEC method including UV, RI and RALS can be used for the simultaneous determination of aggregate content of monoclonal antibodies and antibody fragments. Special about light scattering detectors is that their signal intensity increases with increasing molar mass. This has the two major advantages that light scattering is an absolute method and that light scattering detectors are very sensitive for higher molar masses. Due to its molecular weight dependency, the PSS SLD1000 RALS detector offers high sensitivity also for small quantities of high aggregates and also allows the determination of the absolute molecular weight of the antibodies.





