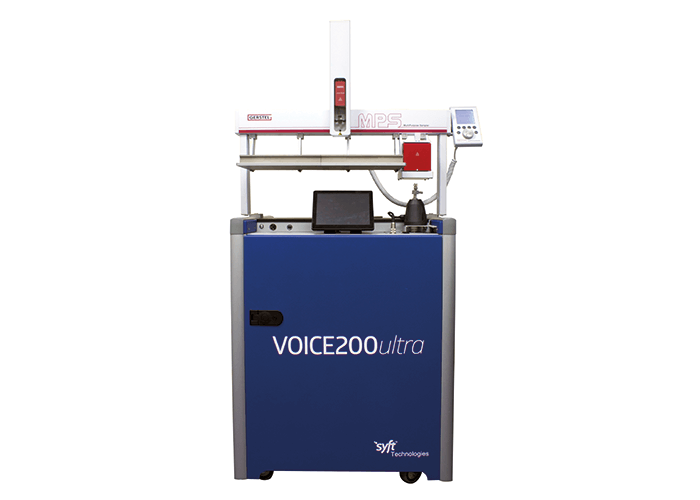

In 2016, the automated SIFT-MS solution was commercialized as the outcome of collaborative research and development by Syft Technologies and Anatune, which integrated and optimized the Gerstel MPS multipurpose autosampler system for use with the Syft Technologies Voice200ultra SIFT-MS instrument. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) is a cutting-edge analytical technique for real-time measurement of trace gases with detection limits in the low parts-per-trillion (ppt) concentration range. The high selectivity achieved by this chromatography-free, direct-analysis technique is achieved by application of multiple, switchable chemical ionization reagent ions coupled with mass spectrometric detection. Automation of rapid SIFT-MS analysis provides unique opportunities for comprehensive, high-throughput sample analysis. The application of direct, ultra-soft chemical ionization enables headspace and gas samples containing routine and chromatographically challenging compounds (such as ammonia, formaldehyde, hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen sulfide) to be analyzed with throughput in excess of 100 samples per hour.
Potential impact
Automated gas and headspace analysis has traditionally been the domain of chromatographic techniques. However, sample throughput with these technologies is limited by the slow chromatographic process itself.By automating SIFT-MS analysis, Syft Technologies and Anatune have developed a very high-throughput headspace and gas analysis system that revolutionizes gas and headspace analysis, providing new opportunities for both contract and R&D laboratories, from environmental analysis to food testing to pharma. Applications enhanced by more rapid analysis include:
- Residual monomer analysis
- Residual solvent testing in packaging
- and pharmaceuticals
- Multiple headspace extraction
- Monitoring of polar and reactive species, including ammonia, formaldehyde, and hydrogen sulfide.

The Nexera-i MT features two independent and dedicated flow lines, one for UHPLC and one for HPLC analyses. Newly developed Analytical Conditions Transfer and Optimization (ACTO) technology minimizes the effect of system volume differences on analytical results. In addition to improving the efficiency and quality of method development and transfer efforts in quality control departments, Nexera-i MT’s dual flow lines also boost operational efficiency. They allow a single instrument to run both HPLC and UHPLC analyses, as opposed to separate dedicated instruments for each.
Potential impact
Nexera-i MT achieves excellent analytical reproducibility when switching from a system with large volume to a system with smaller volume – or vice-versa. It also allows matching of existing HPLC or UHPLC methods run on competitive instrument platforms, automatically compensating for differences in system volume. New software features offer support with transfer of existing HPLC methods to faster UHPLC analyses while assuring high cross-compatibility between old and new method conditions. It can also be used for quick method development in UHPLC mode followed by seamless conversion to HPLC methods (using the incorporated conversion program) for broader applicability.
What the judges say:
“Greatly increases the flexibility of laboratories while reducing complexity. More methods can be done with fewer instruments.”
“Removes barrier to method translation from HPLC to UHPLC.”
More information: www.shimadzu.com/an/hplc/i-series/nexera-i_mt.html
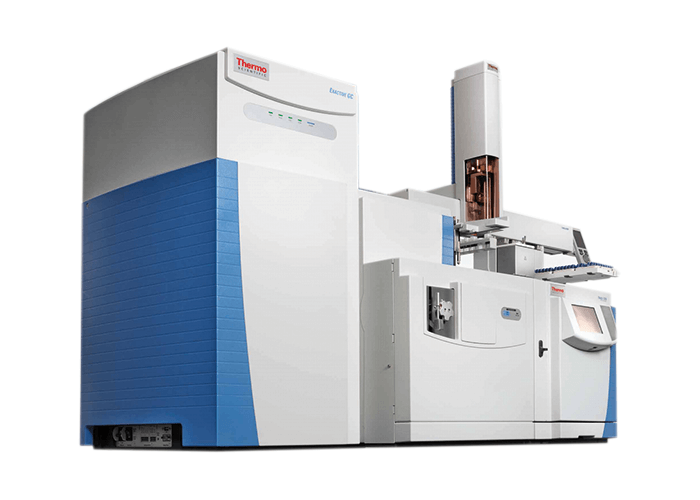

The Thermo Scientific Exactive GC Orbitrap GC-MS system is designed to provide sensitive, routine grade performance for both targeted and non-targeted analysis, along with powerful quantitation. The system offers the quantitative power of a GC triple quadrupole mass spectrometer combined with the unique advantages of Orbitrap’s high resolution, accurate mass technology, allowing new options for routine laboratories to advance their workflows. With the Exactive GC system, users can now acquire high-resolution scan data, mine data, perform retrospective analysis and look for compounds that would otherwise be undetectable with traditional targeted analysis. The system’s capabilities bring additional new benefits to the routine environment, including ease of analytical set-up, broad scope, efficient automatic data processing and retrospective data analysis. In addition to technologies such as time-of-flight and quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry, the Exactive GC provides other analytical options to scientists – allowing selective, quantitative and qualitative analysis from within the same injection, routinely.
Potential impact
Routine laboratories in the fields of food safety, environmental, forensics and anti-doping commonly need high selectivity and sensitivity to detect and analyze increasingly challenging compounds and matrix combinations, which to date has required a range of techniques to accurately screen and quantify compounds. Harnessing the power of the Orbitrap technology, the new system is designed for scientists working in these routine environments who are looking to increase their reach beyond targeted quantitation throughout analysis. Through uniquely high resolving power, mass accuracy, linear dynamic range and sensitivity, the Exactive GC allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of their samples. What the judges say: “Why separate in chromatography, if the mass spec dimension can also distinguish the molecules? Unsurpassed mass resolution, reliable, and easy to use.” More information: www.thermofisher.com/ExactiveGC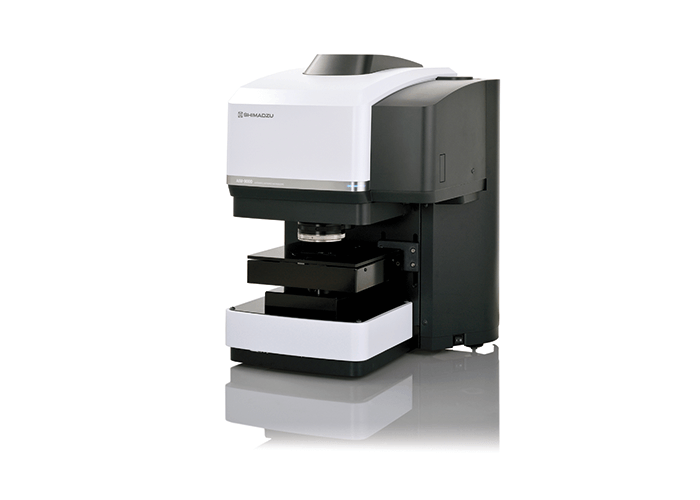
The AIM-9000 offers automation of all necessary steps involved in failure analysis and micro sample evaluation: observation, definition of measurement spots, measurement and identification.
The main features of this grade of automation are:
- a unique wide field camera for automatic zoom-in from eye-size (10 x 13 mm) to contaminant-size (300 x 400 μm)
- Automatic Contaminant Recognition Function to set aperture on measurementspots automatically
- Contaminant Analysis Program to identify the spectrum automatically.
Potential impact
With the AIM-9000, Shimadzu provides an analysis system for all users for quick and easy microanalysis. It targets various industries, including electrical and electronics, machinery and transportation, pharmaceuticals and life sciences, petroleum and chemicals. Enhanced sensitivity and increased ease of operation enable a completely new user experience. What the judges say: “Analysis is just a step to a decision – good or bad, healthy or diseased. This device provides a decision, not just data.” More information: www.shimadzu.eu.com/aim-9000-infrared-microscope-system-unveiling-cause-failuresA multidimensional GC-combustion-isotopic ratio mass spectrometry/triple quadrupole MS prototype (MDGC-C-IRMS/QqQ-MS) was developed and optimized to allow highly accurate δ13C measurement after high-resolution separation using two different GC stationary phases. The low dead-volumes of the C-IRMS system drastically reduce the extra-column band-broadening effect that usually affects commercial GC-C-IRMS instrumentation. The multi heart-cut Deans switch used poses no limitation to the number of 1D peaks that can be transferred to the 2D column and subsequently measured. Finally, the prototype allows the identification, quantification (in MRM mode) and δ13C measurement of target compounds in a single analysis thanks to the simultaneous IRMS/QqQ-MS detection.
Potential impact
The enhanced performance of the prototype system overcomes common issues of commercial monodimensional and bidimensional GC-C-IRMS systems that have so far limited the widespread use of this technique. Monodimensional systems are affected by the low chromatographic resolution arising from the extra-column band-broadening produced by dead volumes in the combustion oven, as well as in the IRMS flow path. δ13C measurements of impure peaks lead to incorrect values, hampering GC-C-IRMS applications for antidoping, geographical origin and natural/synthetic evaluation. Commercial multidimensional systems suffer from a limited heart-cut number per analysis because of retention time shifts. The prototype combines the high resolving power of the multi-cut MDGC with the low IRMS dead-volumes, resulting in accurate δ13C measurements. The qualitative and quantitative capabilities of the QqQ-MS in MRM mode produce an “all-in-one” high-performance instrument that reduces the time and cost for routine applications. What the judges say: “This new MDGC technique improves on commercial systems that limit the number of second dimension fractions that can be analyzed, while also reducing the extra-column band broadening that can limit traditional IRMS performance.” “Could become a key technique in establishing origin/authenticity of samples. So far, such techniques are scarce.”
We have combined, for the first time, an atmospheric pressure gas-phase conversion mechanism with new ceramic coatings to create an innovative interface, called Liquid-EI (LEI). LEI is based on electron ionization (EI) but differs from previous attempts; the vaporization of solutes and mobile phase takes place at atmospheric pressure into a specifically designed region, called the “vaporization micro-channel”, before entering the high-vacuum ion source. The interface is completely independent from the rest of the instrumentation, and can be adapted to any gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) system, as an add-on for a rapid LC-MS conversion. A ceramic liner, placed inside the vaporization micro-channel, acts as an inert, ‘non-stick’ vaporization surface, speeding up the gas-phase conversion of large molecules while lessening possible memory effects.
Potential impact
EI is an unparalleled, well-established tool for the identification of unknown gas-phase molecules. Its extension to a liquid phase, without the drawbacks and limitations that troubled this hybrid combination to date, provide the same unique advantages (library searchable mass spectra, robustness, negligible matrix effects) to LC amenable compounds, opening the door to new, challenging LC-MS applications. Ceramic coatings help to release the heaviest compounds to the gas-phase, improving vaporization efficiency and reducing high-temperature contact time for the most labile substances, bridging the gap between the world of classic LC-MS and GC-MS. What the judges say: “Evidence shows that EI is a great ionization technique for LC-MS. The liquid-EI makes it more practical.” “Electron ionization is no longer limited to the realm of GC-MS! This could help improve the analysis of small molecules in LC-MS.” More information: www.facebook.com/lcmsgroup/
The CLAM-2000* (Clinical Laboratory Automated sample preparation Module) automates the pretreatment of blood or other biological samples before LC-MS analysis. By simply placing blood collection tubes in the system, the CLAM-2000 performs all processes through to LC-MS analysis automatically. Unlike dispensing systems based on batch processing 96-well plates, the CLAM-2000 is completely automatic from pretreatment to analysis, and processes individual samples successively in parallel. This results in uniform pretreatment times between samples without slowing processing speed, and improves data reproducibility and accuracy. Available pretreatment processes include dispensing samples, dispensing reagents, stirring, suction filtration, incubation, and automatic transfer of sample vials to an autosampler after pretreatment.
Potential impact
The new CLAM-2000 is the world’s first system able to fully automate all steps from pretreatment of the sample to LC-MS analysis. It requires only the simple task of placing the blood or biological fluids collection tubes, reagents, internal standards and specialized pretreatment vials in the system. The user-friendly management functions provide a dramatically improved workflow with better safety for clinical research along with higher reproducibility. *For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not available in the USA, Canada, or China. What the judges say: “The CLAM-2000 completely automates sample preparation for clinical samples; this could help prevent user error in labs where accurate analysis is of the utmost importance.” “Sample preparation is the biggest challenge in most analytical methods. Automation is key to addressing this challenge – especially for biological samples.” More information: http://shimadzu.com/an/lcms/clam/index.html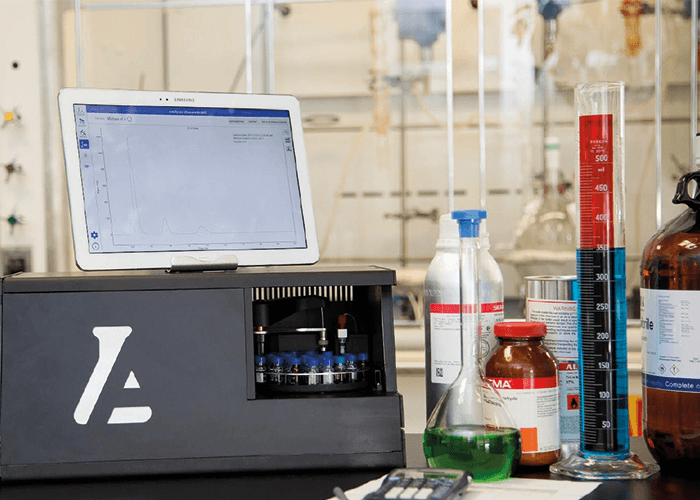
The Alltesta Analyzer is compact and lightweight (200 x 330 x 180 mm and under 10 kg), and is operated by a user-friendly touch-screen interface that requires only a tablet for operation – no desktops, monitors, or cables. The analyzer features a patented wash system, adjustable needle depth, and a flexible communication protocol (RS485/RS232/CAN). Its LED-based detector delivers a narrow, intense bandwidth, and uses a long-lasting, low-noise light source for high sensitivity. The short internal flow path volume minimizes band spreading, and only very stable materials (PEEK, PTFE and quartz) contact the fluid. The Alltesta pump precisely delivers fluid at flow rates from 0.10 ml/min to 4.0 ml/min using up to 5000 psi (350 bar) of continuous pressure. The Analyzer comes preloaded with over 1,000 methods for a diverse array of compounds and does not require comprehensive knowledge of chemistry or chromatography. It is backed up with lifetime free method development screening.
Potential impact
The Alltesta Analyzer overcomes the challenges of downscaling hardware and reducing solvent consumption, which have previously hindered the development of a portable LC system despite advances in stationary phase chemistry, flow rate hardware, and particle miniaturization. The Alltesta Analyzer represents a novel approach to compact HPLC. Targeting applications in pharmaceutical, agricultural, and consumer goods, the Alltesta Analyzer has the potential to transform how chromatography is performed in myriad fields and industries. What the judges say: “Simplifies HPLC analysis for non-specialists working in key applications.” “A very simple LC system that has great potential in labs where more standard, high-end instruments are not required.” More information: http://www.sielc.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Analyzer-Brochure-for-the-Web.pdf
The RamTest is a state-of-the-art handheld analyzer that utilizes the most recent advances in Raman technology. This easy-to-use, lightweight, and ergonomic unit offers best-in-class analytical performance and unmatched cost-effectiveness. The superior performance is achieved by combining 532 nm laser excitation (unique for handheld Raman) with the breakthrough methodology to reduce the impact of fluorescence on Raman measurements. RamTest benefits include:
- 5–16 times faster analysis, improved analysis accuracy, dramatically reduced detection limits
- two-fold reduced unit cost
- best-in-class spectral resolution (4–6 cm-1) and spectral range (120–4000 cm-1)
- Superior performance in water and most organic solvents
- Ability to measure delicate (for example, carbon nanotubes) and dangerous (for example, explosive) samples by utilizing up to 5–16 times reduced laser power (compared to conventional 785 and 1064 nm instruments) without compromising analytical quality.
Potential impact
RamTest enables dramatic improvement of Raman analysis business cases for a great deal of applications in the field, laboratory, quality control, process measurements/PAT. The RamTest opens up new applications areas for Raman spectroscopy, including:- analysis of biologics/biopharmaceuticals in aqueous solutions
- characterization of complex multicomponent mixtures
- automated quantitation of analyte concentrations in aqueous solutions using 3200–3400 cm-1 OH-stretching bands of water for normalization (unattainable with the other handhelds on market)
- detection of ammonia and other compounds previously considered ‘hard- or impossible-to-detect’ with handheld Raman
- carbon nanotubes structural characterization/ quality control
The VGA-101 is a next generation vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) benchtop spectrometer engineered to meet the needs of customers with advanced gas chromatography applications. The VGA-101 features an expanded wavelength spectrum and a higher allowable maximum operating temperature. An expanded wavelength spectrum of 120–430 nm provides unique selectivity for complex structures, such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The ability to operate the VUV detector as high as 450° C allows GC×GC analysis of high boiling point compounds. Engineering advancements have also enabled the VGA-101 to be placed in-line with other GC detectors for new data correlation and analytical insight.
Potential impact
The VGA-101 provides new analytical capabilities to a number of industries including oil and gas, forensics, fragrances and flavors, petrochemical, specialty gas, and life sciences. Customers in the oil refining and petrochemical industries now have a reliable tool for analyzing high boiling point fuel samples containing complex hydrocarbon mixtures. The expanded wavelength spectrum opens new possibilities in characterizing isomeric compounds with extensive branching or ring structure that are difficult to distinguish with alternative methodologies. Hyphenating with mass spectrometry and other GC detectors opens the door to building rich data sets that are correlated unlike any in the past. What the judges say: “The VGA-101 detector builds upon the last great GC detector from VUV Analytics by expanding the temperature range, which enables the analysis of higher boiling point compounds.” “Extends VUV to a practical operating temperature range for GC×GC.”| “Truly novel selectivity in GC, combining the strengths of separations and spectroscopy for the entire range of GC amenable species.” More information: www.vuvanalytics.com
ZipChip allows for direct analysis of complex biological samples providing sample preparation, capillary electrophoresis separation and direct electrospray for MS detection, all on an integrated microfluidic device. ZipChips are compatible with a broad range of analytes from small molecule metabolites and amino acids, through peptides and intact proteins, antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates. ZipChip is deployed from fundamental academic research as well as in the biopharmaceutical industry from early stage research through to monitoring of growth media and final biotherapeutics in production. With intact proteins and antibodies, ZipChip gives characterization of intact molecules in a near native state that is unique and not presently available with other MS-compatible techniques.
Potential impact
The rapid expansion of the life sciences market over the past few decades is driving the demand for increased analytical capabilities. ZipChip addresses some of the most essential areas, from analysis of complex intact proteins to the burgeoning science of metabolomics. Its simplicity of analyses, minimal sample preparation, and delivery of unique data is creating demand from research labs through each critical step in bio therapeutic development through bioprocessing for production. ZipChip’s end-to-end speed, combining minimal prep with analysis times of 2–3 minutes suggests dramatic productivity enhancements and the study of processes that would have been impractical with traditional techniques. By incorporating ZipChip into the life science analysis process, we are dramatically improving what users can see with their MS instruments; transforming time-consuming sample runs into fast, everyday analyses. What the judges say: “By providing a platform for easy coupling of high performance capillary electrophoresis chips to mass spectrometers, the ZipChip offers very effective sample introduction to MS beyond standard LC methods.” “An integrated front-end CE solution for MS, including portable MS.” More information: http://908devices.com/products/zipchip/
Typically, Raman microscopy needs to be performed on flat surfaces. With Renishaw’s LiveTrack technology – incorporated in Renishaw’s new inVia Qontor confocal Raman microscope – this is no longer the case. LiveTrack removes the need for manual focusing, pre-scanning or sample preparation (to give a flat surface). Uniquely, LiveTrack provides continuous feedback to the sample stage, which adjusts to follow the height of the sample. Users can track the surface of a sample, live, while acquiring surface or subsurface Raman data. The resulting Raman image and surface topography is viewed in 3D. The range of focus travel is exceptional and can be used across the whole horizontal and vertical travel of the microscope stage. LiveTrack opens the door to a new era of applications and measurement simplicity.
Potential impact
LiveTrack technology significantly reduces overall experiment times and makes analyzing even the most complex samples easy. Now, Raman imaging is no longer limited by a sample’s topography. Efficiency is improved and reliable. Reproducible spectra can be rapidly obtained from a whole range of samples, covering a diverse range of application areas, including those not previously possible. Example application areas include rocks and minerals, pharmaceutical tablets and tissue biopsies. Focus is maintained during dynamic measurements, such as heating, cooling or melting, expanding the range of measurements to which Raman spectroscopy and imaging can be applied. What the judges say: “Most imaging techniques require a flat surface, but most real samples are complex. LiveTrack allows imaging of real samples as they are, greatly extending the application of Raman imaging.” “The most exciting thing about the LiveTrack is the wider range of samples that can be studied by Raman imaging. Another great feature is the ability to make dynamic measurements during temperature or phase changes.” “Sample preparation for Raman is complex and may change the sample. With this method, Raman imaging becomes easier, more reliable – and more real.” More information: www.renishaw.com/livetrack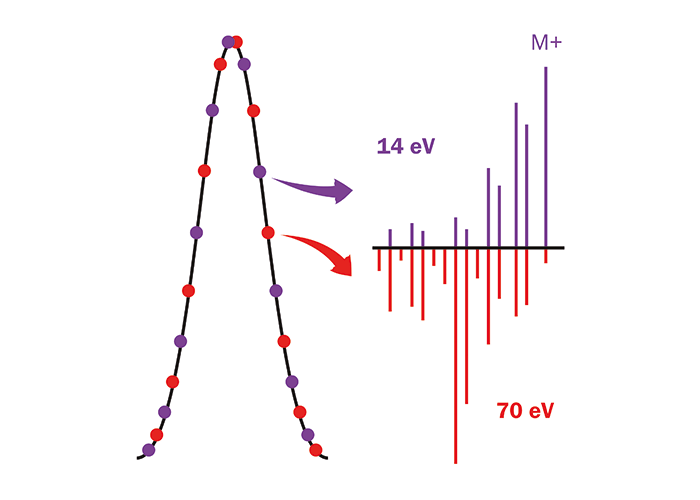
Tandem Ionisation technology for time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF-MS) means that a single GC or GC×GC run can provide all the information needed to fully characterize a sample for target compounds and unknowns. Tandem Ionisation works by generating two electron ionization (EI) mass spectra from a single peak by rapid switching between conventional 70 eV ‘hard’ ionization and ‘soft’ ionization at 10–16 eV. Crucially, acquisition of the soft ionization spectra is not associated with the inherent loss of sensitivity historically associated with soft EI, and unlike other soft ionization approaches does not require switching of ion sources or use of reagent gases. In addition, operation of Tandem Ionisation is fully automated within the software package for Markes’ BenchTOF-Select time-of-flight mass spectrometer, meaning that laboratory workflow is unaffected.
Potential impact
Tandem Ionisation allows regular library-matching of 70 eV spectra against commercial libraries, such as NIST or Wiley, alongside all two key benefits of soft ionization – discrimination between structurally similar isomers, and confirmation of the identity of compounds with weak molecular ions at 70 eV. Providing these capabilities within a single GC run has the potential to change the way that analysts approach GC and GC×GC analyses – it is already proving valuable for identifying long-chain alkanes in petrochemicals, and for discriminating between structurally similar terpenoids in fragranced products.
What the judges say:
“All information needed for reliable compound information is contained in one run. Saves days of working and waiting time because it eliminates the need to re-configure complex GC-MS instruments.”
“Tandem Ionisation technology allows two different MS spectra to be collected simultaneously, which should greatly enhance the analyte identification capabilities of the technique.”
“Combining hard and soft ionization offers unparalleled identification opportunities in GC.”
More information: http://chem.markes.com/TI
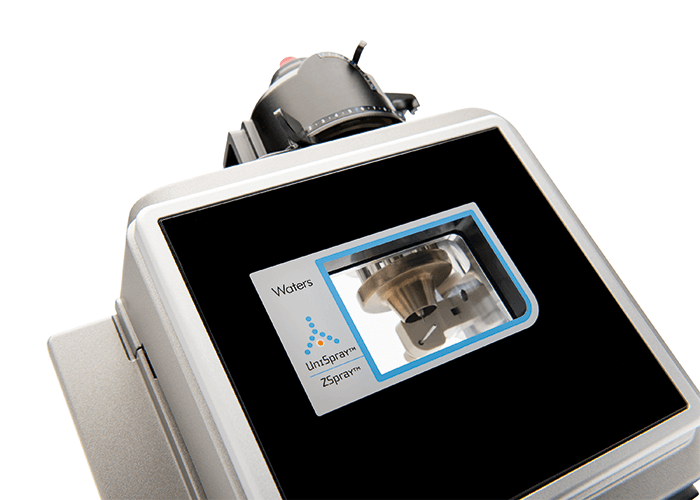

High flow rate ESI remains the preferred ionization technique for LC/MS analyses because it offers the most facile coupling for a wide range of analytical flow rates. However, when compared to nanospray ionization, ESI is known to suffer from poor ionization efficiency at high flow rates. UniSpray is a novel ion source for mass spectrometry that incorporates unique aerodynamic features. The resulting “cylinder in cross-flow” geometry demonstrates significant enhancements in both ionization efficiency and compound coverage when compared to conventional, nebulizer-assisted ESI sources.
Potential impact
UniSpray has the potential to increase the number and type of compounds that can be detected by mass spectrometry in a single run while simultaneously enhancing sensitivity. Therefore, Unispray could allow the consolidation of multiple methods into a single analysis, giving laboratories the opportunity to optimize efficiency, as well as allowing users to see a more complete picture of what is present in their samples. What the judges say: “Improves ionization efficiency of ESI, which is key to improving performance of ESI-MS.” “The UniSpray brings ESI at higher LC flow rates more in-line with the benefits of nanospray by improving ionization efficiency and increasing compound coverage.” “Sensitivity is always an issue, just like ease of use. This development combines easier to use high flow rates with the better sensitivity of lower flows.” More information: www.waters.com
The Agilent Intuvo 9000 GC System changes the paradigm in GC, comprising hardware, software, consumables and supplies. Intuvo embodies three transformational innovations:
- Direct conductive heating is used to temperature program the entire flow path and analytical column. This uses less than half the power of a conventional air bath oven, takes about half the laboratory bench footprint, and heats and cools much faster, improving throughput.
- Intuvo’s click-and-run, leak-free connections replace traditional column nuts and ferrules. An audible and tactile ‘click’ indicates when the correct connection has been made. Unplanned downtime and associated business disruption, so often encountered from leaks arising from incorrect connections, are eliminated.
- Intuvo’s no-trim columns are designed with a simple, disposable Guard Chip, which serves as a retention gap. The Guard Chip traps unwanted material from depositing on – and potentially damaging – the head of the column. Column trimming is eliminated altogether, enhancing productivity.




