What exactly does your team do – and what analytical technology do you rely on?
In short, my team develops chromatographic methods to analyze the quality attributes of the therapeutic antibodies we develop. Our workhorse analytical tools are U/HPLC and LC-MS/MS systems.
What keeps you motivated?
As a company, our priority is creating safe, effective and accessible drugs for the patients who need them. The safety of a biological drug relies on the quality attributes of the antibody, so having sensitive and accurate methods to analyze them is of outmost importance during the drug development phase. It is incredibly rewarding to feel that our work is contributing directly to patient safety.
My favorite part of the job is when we are able to improve a method to generate less waste, be more analyst-friendly and less time-consuming – all while still generating high-quality results. Ultimately, that enables us to develop projects faster and deliver safe drugs to patients at an affordable price. We are constantly looking for technological innovations that help us to achieve that.
Why is N-glycosylation so important in biopharma analysis?
N-linked glycosylation describes the attachment of oligosaccharides (sugars) to a protein, via an asparagine residue. We pay very close attention to N-glycosylation of biologics – the composition of the sugar chains attached to the drug molecule is one the key quality attributes for therapeutic antibodies.

N-glycosylation strongly affects the way the drug interacts with its target (for example, cancer cells). It determines how efficient it is in its therapeutic action, how long it remains active and how long it circulates in the bloodstream. In addition, making sure that the N-glycosylation stays the same during development, through clinical trials and onto the market helps to minimize the possibility of any adverse reaction. It is crucial to carefully monitor the N-glycosylation throughout project development and then in the production process to ensure that patients always receive safe, high-quality medicine.
What challenges does glycan variant analysis typically present?
There are a number of powerful, gold-standard methods for the accurate analysis of antibody N-glycosylation. These methods typically require sample purification followed by multi-step preparation of some sort; for instance, proteolytic digestion or glycan separation and labeling, several clean-up steps, and finally UPLC or LC-MS analysis. All of these steps can be automated, of course, but it still takes significant time. The ideal approach would keep the reliability and high quality of results while simplifying and accelerating the workflow.
You’ve used a number of different LC columns over the years. How is the FcR column different?
By using an FcR HPLC column, we can make the whole process much simpler. For a significant number of therapeutic antibodies, interaction with the Fcγ receptor is crucial for their activity. This interaction is strongly dependent on the type of N-glycosylation. By making good use of the unique characteristics of the TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR column, which uses the Fcγ receptor as the ligand, we are able to get information on the N-glycosylation of the antibody and its biological activity. The resulting pattern of chromatographic peaks strongly correlates with the N-glycosylation composition.
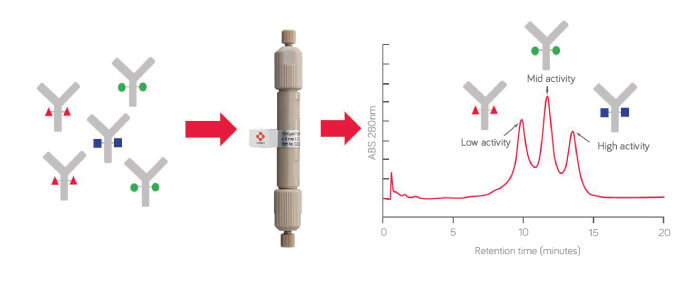
The accuracy of the data really surprised us. We could predict the content of galactosylated glycans with less than five percent error in most cases, compared with the orthogonal method – HILIC-UPLC using released and labeled N-glycans.
The method was sensitive enough to use low microgram amounts of sample and, on top of that, we got virtually the same results regardless of whether we used highly purified sample or the antibody still in the cell medium. And that means we can perform high-throughput and highly informative screening of clones, cell culture conditions and lead molecule selection with minimal sample handling. Not to mention that the lack of sample preparation makes this approach cost-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Given these characteristics. I am certain that the FcR column will be extensively used in our current and prospective biosimilar development projects.
How else could the column be used?
As well as targeted screening for activity and glycosylation, I believe that the column has potential in a number of areas. Estimation of binding affinity on non-purified samples is one thing that comes to mind. The fact that the Fc region of the antibody interacts with FcR can be used to detect antibody fragmentation or changes in the quaternary structure. FcR could make a great ligand for antibody purification, so a preparative-scale FcR-IIIA column is something I’d be interested in exploring. I imagine that our colleagues in the Quality Control department might find some new uses for the column too; for example, in one of the batch-release methods.