Produced by SCIEX
The ZenoTOF 7600 mass spectrometer is an orthogonal quadrupole time of flight (QTOF) mass spectrometer with a Zeno trap. With the new trap/release setup, ions at the end of the collision cell are trapped in a short linear ion trap. Voltages are then applied, causing the ions to be released so that lower m/z ions entering the TOF accelerator catch up with heavier ions at higher m/z, allowing all ions to meet before they get pushed in the TOF extraction region. The result is a substantial gain in sensitivity (≥90 percent duty cycle) without the loss of mass resolution or accuracy – leading to improvements on MS/MS spectral quality. In addition, SCIEX’s new reagent-free EAD (electron activation dissociation) cell offers an alternative fragmentation strategy, which preserves labile modifications.
Potential impact
The improvements in MS/MS sensitivity offered by the Zeno trap coupled with the benefits of tunable modes of fragmentation with EAD should help scientists address analytical challenges across many markets. According to SCIEX, the ZenoTOF 7600 can quantify up to 40 percent more proteins and analyze samples five times faster for large biobank studies. Moreover, EAD fragmentation could allow researchers to better understand how proteins are post-translationally modified – an important but challenging area in biomarker research. The system can also be used to fully characterize an individual lipid from a single spectrum using EAD fragmentation, which may enable the discovery of novel lipid markers for cancer and inflammatory disease.
What the judges say…
“This is a new generation QTOF mass spectrometer from one of the industry leaders in QTOF technology. The improvements in speed and sensitivity are clearly huge leaps over previous generations – as is the new EAD cell to generate fragment ion mass spectra.”

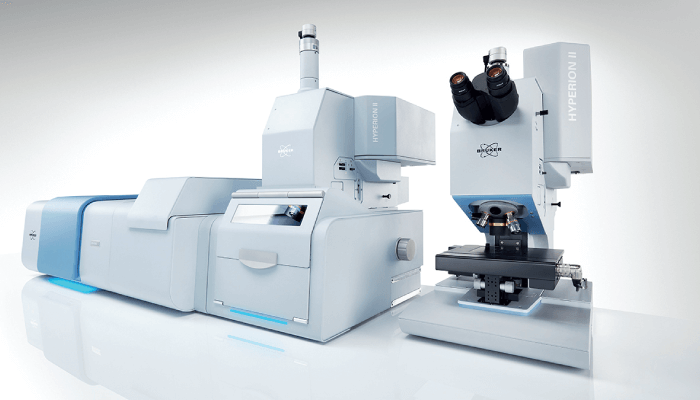
Produced by Bruker Optics
The HYPERION II FTIR QCL Imaging Microscope maintains the versatility of the original HYPERION microscope and expands its list of features with quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) and an optimized beam path for imaging applications. The HYPERION II can be equipped with a low magnification objective (3.5x) to enable fast imaging on large areas (for example, in tissue imaging or surface analysis). And the addition of a TE-MCT allows for sensitive MCT-measurements without the need for liquid nitrogen. Finally, the design has been streamlined to better represent the new features and match the style of the INVENIO-platform.
Potential impact
The combination of FT-IR and QCL technology in one instrument should create new opportunities for researchers in a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, forensics, microplastics, polymers and plastics, semiconductors, and more. Users simply need to collect an FT-IR spectrum and select the wavelengths for investigation using QCL to rapidly create chemical images.
What the judges say...
“A great combination of IR and ILM that should open up some interesting opportunities for combinatorial analysis of a range of materials.”
“Access to a quantum cascade laser for imaging microscopy appears to be a powerful combination!”

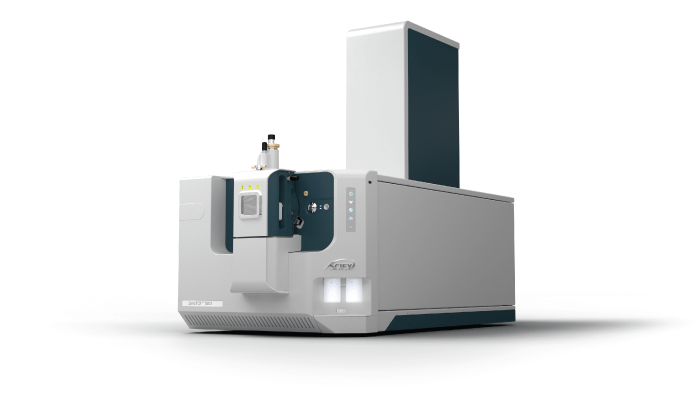
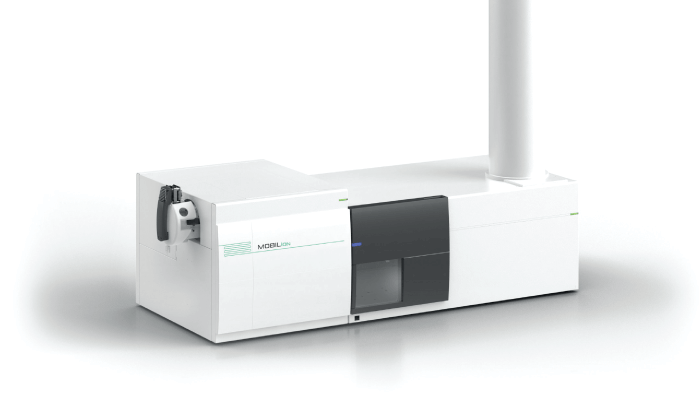
Produced by MOBILion Systems, Inc.
MOBIE is MOBILion’s first SLIM-based (structures for lossless ion manipulation) high-resolution ion mobility (HRIM) product on the market – and it aims to accelerate and simplify the workflows of challenging analyte classes, including peptides, proteins, lipids, and glycans. SLIM stands out from other ion mobility platforms with its 13-meter path length and serpentine electrode patterns (on standard printed circuit boards) – in a benchtop instrument. The longer path length enables a much higher resolution and the separation of highly similar molecules, greatly improving reliability and reproducibility in the lab.
Potential impact
There’s a growing demand for instruments that can characterize more complex therapeutic systems and identify biomarkers in the biopharma drug development space. And according to MOBILion, MOBIE can analyze 5-60 times faster than conventional separation methods, such as LC. MOBIE is integrated with Agilent Technologies’ 6500 line of Q-TOF mass spectrometers, which combines high ion mobility separation performance with mass spectral fidelity.
What the judges say...
“The SLIM system has the potential to offer high resolution gas phase separations in small footprints compared with conventional systems. The applications are very broad and could impact a large number of areas.”
“One of the true innovations in ion mobility based separations.”

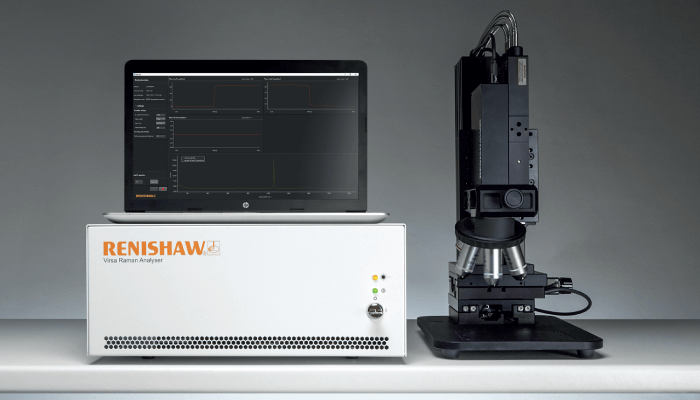
Produced by Renishaw Plc.
Renishaw's Virsa Raman analyser allows users to analyze samples away from the confines of the laboratory microscope, using remote fiber-optic probes, thereby expanding the use of Raman spectroscopy to new samples, applications, and environments. The Virsa system has LiveTrack focus-tracking technology and a new Monitor software module, which together enable real-time analysis on large samples with irregular surfaces – such as those that move (on production lines for example) or change shape as they undergo phase changes.
Potential impact
The Virsa Raman Analyser is portable, allowing users to analyze samples in their native environment. Large or immovable samples that can’t be placed under a microscope, or those contained within vessels, can be measured with laboratory-grade performance, high sensitivity, and high spectral and spatial resolution. Renishaw hopes that the system acts as a bridge between research/laboratory Raman measurements and in-field applications – expanding the range of applications and uses of Raman spectroscopy.
What the judges say…
“Raman often suffers because the sample must be flat. This solution builds on previous innovations to allow automatic real-time analysis on samples with irregular surfaces.”
“A remote sampling probe for Raman spectroscopy is a welcome addition for many labs.”

Produced by Markes International
Markes’ multi-gas enabled system has been independently certified for use with hydrogen as well as helium and nitrogen carrier gases. Switching to hydrogen produces the same data quality as helium, but at a greatly reduced cost. The implementation is straightforward too, as commercially available software can be used to translate the GC method from helium to hydrogen.
Potential impact
Switching from helium to hydrogen carrier gas protects laboratories against future helium shortages and is more sustainable because high-purity hydrogen can be generated from water. Hydrogen offers faster chromatographic separations, shorter thermal desorption methods and lower-temperature separations than helium, increasing laboratory throughput, extending consumables’ lifetimes and extending maintenance intervals. Finally, switching from helium to hydrogen saves up to 90 percent per cylinder and a hydrogen generator eliminates the costs of cylinders.
What the judges say…
“Moving from helium to hydrogen for TD makes economic sense, with helium prices increasing rapidly. Many labs who have become frustrated with helium availability will find this product to their liking.”

Produced by Waters Corporation
With pre-defined analytical methods, guided workflows, auto-calibration and auto-tuning, analysts can use Waters’ BioAccord System with ACQUITY Premier to monitor critical quality attributes of biotherapeutics and assess the processes that make them, while decreasing risk. The system incorporates the ACQUITY Premier LC inlet featuring MaxPeak high performance surface (HPS) technology, which eliminates analyte/surface interactions and thereby improves recoveries of hard-to-detect sample analytes. The result, according to Waters, is improved assay-to-assay reproducibility.
Potential impact
Biologists and chemists who once had to send samples to a laboratory and await results can, with Water’s system, instantly monitor critical quality attributes of challenging biotherapeutics in development. With this information, drug companies may be able to cut costs and delays. Additionally, the system automatically monitors its own performance, improving productivity by maximizing system uptime and minimizing re-analysis.
What the judges say…
“The BioAccord has been a popular platform for biopharma analysis. This improved platform appears to be a nextgen system with improved systems capabilities – closer to plug-and-play for biopharma.”

Produced by Waters Corporation
The 200,000 FWHM resolution achieved by the SELECT SERIES MRT is the result of multiple reflections of the ion beam, which increase the length of the flight path to 47m, while maintaining a manageable instrument footprint. This, in combination with multi reflecting time-of-flight (MRT) technology, results in high resolution over a broad mass range and routine ppb mass accuracy, enabling highly detailed structural characterization. The system was introduced for MS imaging and can be equipped with enhanced desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) imaging sources. Together, these technologies enable scientists to explore molecular structure and function through the precise identification and localization of individual molecules in samples.
Potential impact
SELECT SERIES MRT aims to help scientists increase their understanding of the spatial localization of molecules and their mechanisms of action in various scientific fields, including pharma, biomedicine, natural products research, and materials research. For example, a researcher trying to understand how an investigational oncology drug interacts with its intended target, such as a specific brain tumor receptor, could use the SELECT SERIES MRT to do so much faster – at speeds up to 10 Hz without compromising mass accuracy or resolution.
What the judges say...
“This is a really exciting multi-reflecting ToF mass spectrometer that not only allows higher resolution, but does so in a compact space. This is one instrument to watch.”

Produced by Thermo Fisher Scientific
The Orbitrap Exploris GC 240 MS has a resolving power of 240,000 that, in combination with its wide dynamic range, should deliver increased flexibility, speed, and accuracy in a variety of research applications. The system offers MS/MS capability for compound structural information, and both electron and chemical ionization without system venting – for fast and accurate analysis.
Potential impact
The Orbitrap Exploris GC 240 MS aims to accelerate scientific discovery in academic, industry research, government, and omics laboratories. The system provides the flexibility to tackle a diverse range of analytical challenges, including identification of unknown compounds across a spectrum of applications – from extractables and leachables studies to metabolomics.
What the judges say…
“An integrated GC system coupled to high resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry is a nice advancement over previous generations. It is better integrated than previous generations too – and in a smaller footprint. I expect that this will be a popular instrument.”

Produced by ACD Labs (Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc.)
Spectrus JS brings the ACD Lab’s popular NMR data processing tools from the desktop to the browser, providing a complete toolset for processing 1D and 2D NMR data without the heavy CPU requirements and lengthy installers needed to use modern desktop NMR processing software. The easy-to-access interface makes Spectrus JS suitable for casual users and expert spectroscopists alike. For the first time, organizations can host vendor-agnostic NMR processing applications and deliver them to users over their network – all individual users need to do is type the URL into their browser and log in.
Potential impact
For facility managers and those involved in the management of open access labs, Spectrus JS will allow easy deployment on a single hosting server/computer. Additionally, being able to access the software remotely will allow for better use of instrument time – enabling a shift to more flexible work environments. In academia, students can access Spectrus JS on their own devices or shared public computers, enabling educators to better equip their students by providing hands-on experience processing NMR data.
What the judges say…
“All-in-one software is always appreciated in core facilities. And this will be a popular NMR software system for academic and other large facilities because of its flexibility.”
Produced by Thermo Fisher Scientific
Proteome Discoverer 3.0 is a piece of MS software that, when combined with MSAID’s CHIMERYS search engine, uses artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning to substantially increase peptide identification and quantitation capabilities for proteomics researchers. Instead of assuming that all peaks in a tandem mass spectra are derived from a single peptide, as most software does, Proteome Discoverer identifies a minimal set of peptides that can explain the acquired tandem of mass spectra.
Potential impact
AI allows deeper mining of proteomic data, not only improving proteomic coverage, but also expanding the possibilities for scientists to acquire and apply their data. According to Thermo Fisher Scientific, the software provides a 1.7-fold increase in the peptide identification rate and 1.3-fold increase in the protein identification rate, which should enable more efficient data acquisition, helping scientists generate more biological insights from their data.
What the judges say…
“This appears to be a first generation proteomics software platform based on AI technology for more efficient and accurate protein identification. Proteome Discoverer is already an industry standard for the field; I expect many customers will upgrade their systems to version 3.0.”

Produced by KAYCHA LABS
Hop Latent Viroid (HLVd) is a single-stranded, circular strand of RNA that can cause disease in many plants, including cannabis/hemp. Plants infected with HLVd may or may not show symptoms and the disease can be dormant in a plant for extended periods of time prior to showing symptoms. Kaycha Labs’ HLVd test uses a type of PCR called loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), which, when tagged with carboxyfluorescein (FAM) and biotin, creates dual-labeled products that can be visualized with lateral flow assays (LFA). If a sufficient number of dual labeled products are present, a test line becomes visible within 5-10 minutes.
Potential impact
HLVd greatly reduces the quality and quantity of the flower in the infected plant. During the vegetative stage, plants grow shorter with smaller leaves and tighter node spacing. Flowering plants will have smaller buds with much fewer trichomes. Over time, yields can be reduced up to 70 percent, with a loss of potency and terpene production up to 35 percent. MH Verify’s field test kit makes it easier for growers to detect plant pathogen contamination rapidly.
What the judges say…
“This technology could benefit the economics of the cannabis/hemp industry. And it seems to be fairly simple, easy to implement technology.”

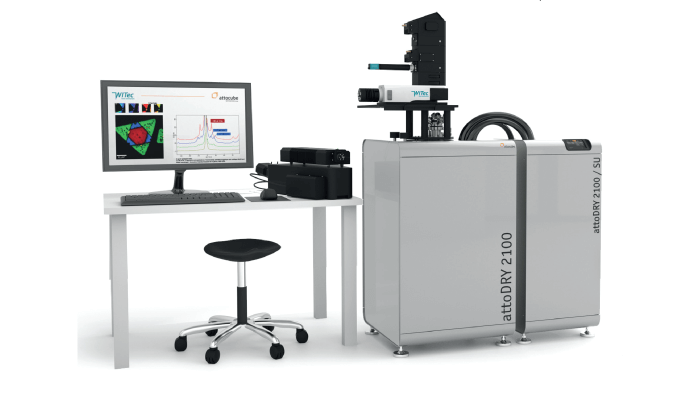
Produced by WITec GmbH and attocube systems AG
WITec and attocube’s cryoRaman makes Raman microscopy at the edge of absolute zero truly accessible for the first time by integrating a Raman imaging system with a cryogenic sample chamber. The technology offers VIS to NIR excitation lasers, 1.8–300 K operating temperatures, high magnetic fields of up to 12 T, cryogenically compatible Raman-specific objectives, and a precise piezoelectric scan stage. Other options include precise software-controlled laser power adjustment, automated switching between optical microscopy and spectroscopic imaging, multi-wavelength excitation capabilities, automated spectrometer calibration light source and routines, time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) modes, low-wavenumber Raman peak detection, and full polarization control in excitation and detection.
Potential impact
Interest in cryogenic Raman imaging has expanded beyond the initial core of graphene and carbon nanotube research groups, which drove the development of cryoRaman. Research on phase-transitions and emergent properties of novel low-dimensional materials will benefit from cryoRaman’s high magnetic field options, which are ideal for investigating transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) and van der Waals heterostructures. Possible applications of these materials include the new generations of transistors, photo detectors, light-emitting diodes and photovoltaic cells.
What the judges say…
“Looks interesting for analysis at cold temperatures – it will be good to see what info comes out of this!”

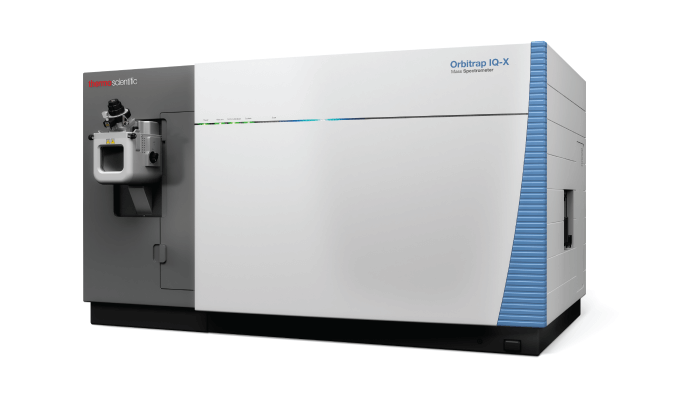
Produced by Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Fisher Scientific’s Orbitrap IQ-X Tribrid MS features software that enables real-time library search to address the complexities of small-molecule identification. The local and customizable library can be used to selectively detect and characterize unknown compounds that are structurally related to known compounds. There’s also an ultraviolet photodissociation option, which provides insights on lipid double-bond localization and site specific glucuronidation; while the 1,000,000 resolution option enables fine isotope detection and improved confidence in results.
Potential impact
The Orbitrap IQ-X Tribrid MS aims to allow small molecule researchers – both in academia and the pharmaceutical industry – to confidently perform a range of applications, including metabolomics and lipidomics research, leachable/extractable impurities identification, and forensic toxicology. The real-time library search technology provides simultaneous spectral searching to increase confidence in metabolite identification and characterization, and improve the structural analysis of isomeric species. Overall, the technology should reduce the number of compounds without MSn spectra and increase the number of compounds identified.
What the judges say…
“This is probably the best platform currently for untargeted metabolomics as the IQX enhances metabolite identification – one of the bottlenecks in metabolomics.”

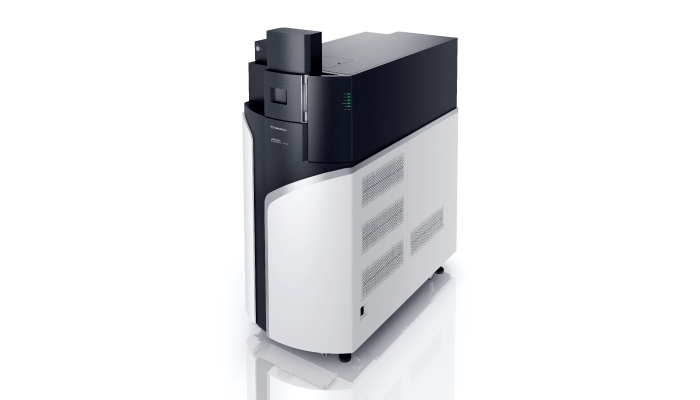
Produced by Shimadzu Corporation
Shimadzu’s DPiMS QT allows researchers to analyze small quantities of sample (liquid or solid) without sample preparation and without LC separation with HRMS. Moreover, thanks to the ease of switching between probe electrospray ionization (PESI) mode or LC-ESI-MS mode, it can provide a wide range of analytical methods – from rapid screening to quantification (using LC-MS analysis).
Potential impact
DPiMS QT will be useful for quick screening in the forensic toxicology field, as well as in the food industry. It reduces the time required to analyze blood, urine, and other biological samples with conventional methods by approximately 50 percent, according to Shimadzu.
What the judges say…
“An exciting sampling interface that reduces sample usage and speeds up analysis times.”

Produced by SCIEX
The development of increasingly sophisticated biopharmaceutical therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), mAb variants, and gene therapies, requires rapid measurement and monitoring of critical quality attributes throughout the development continuum. The SCIEX BioPhase 8800 is a multi-capillary system for CE-SDS analysis that processes eight samples simultaneously – helping scientists understand molecular liabilities more quickly in their efforts to develop and manufacture robust and stable biologics.
Potential impact
Biopharmaceutical manufacturers are transitioning to more innovative biologicals; samples are becoming more numerous and more complex – but results are still needed quickly. By processing eight samples simultaneously, the BioPhase 8800 can, according to SCIEX, reduce experiment design times from one month to as little as a week. How? Because researchers are able to rapidly quantify critical quality attributes for large sample sets, which delivers consistent, comparable data throughout the pipeline – from R&D to bioprocessing to QA/QC.
What the judges say…
“A nice, higher throughput CE-SDS system incorporating multi-capillary analysis.”