Work performed in conjunction with the Molecular Structure Group, IBMC, University of Porto, Portugal
Introduction
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a commonly used tool in the biological sciences. Typically, it is used to measure the molecular weight of an unknown sample by referencing the elution time of the unknown against that of standards of known molecular weight. This can be done with a single concentration detector such as UV or refractive index (RI). Advanced multi-detector SEC systems now include up to four detectors in series for maximum sensitivity; including UV, RI, light scattering and intrinsic viscosity detectors. Light scattering detectors allow the measurement of molecular weight without the need for column calibration.Intrinsic viscosity (IV) is a measure of the contribution of a single molecule of a solute to the overall viscosity of the solution. More intuitively intrinsic viscosity is a measure of molecular density and, more specifically, is inversely proportional to density. Structural changes inevitably result in a change of volume occupied by a molecule and, consequently, its density. Therefore, changes in structure will be reflected in changes in intrinsic viscosity. The Einstein equation [1] combines measurements of intrinsic viscosity and molecular weight to calculate a hydrodynamic radius.
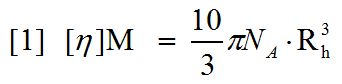
As is clear from the equation, when a structural change occurs, the change in intrinsic viscosity will always be greater than the accompanying change in hydrodynamic size. It is important to note that, although the term hydrodynamic size is used in both DLS and viscosity measurements, the value will always be slightly different as the derivation of the value is entirely different. The soluble portion of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (sRAGE) is a non-globular 34 kDa protein. Studies have shown that this protein undergoes a significant conformational change in the presence of calcium. In this application note, intrinsic viscosity measurements were performed on the sRAGE protein to establish whether the detector was able to detect and characterize the conformational change induced by the presence of calcium. Light scattering molecular weight measurements were also performed. Data are also presented showing that the conformation of sRAGE changes in the presence and absence of calcium. The data include measurements of the fluorescence of tryptophan which changes with the local environment and also temperature trend measurements by dynamic light scattering, which show a shift in aggregation point, also indicating a change in structure.
Methodology
The sample was prepared and measured in 20 mM Tris buffer with 150 mM NaCl. 40 mM CaCl2 was added to the mobile phase for measurements in the presence of calcium. 10% acetonitrile was added to the SEC mobile phase to improve the separation quality. The separation was performed on a GE Superdex™ 75 column.Results
The chromatography ran very well with excellent peak shape for the sRAGE both in the presence and absence of calcium. Chromatograms of the two measurements are shown in figure 1. The molecular weight, intrinsic viscosity and hydrodynamic size were measured on duplicate chromatograms and the results are shown in table 1.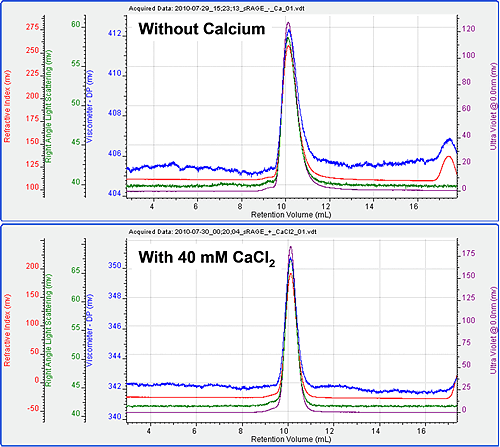
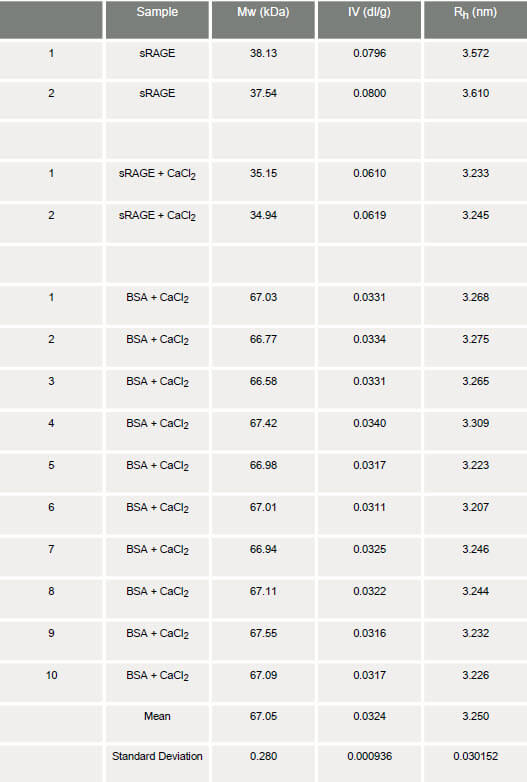
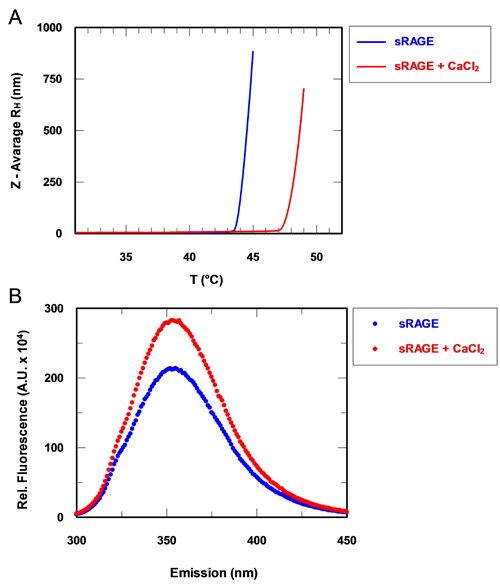
From the table, it can be seen that there is a notable difference in intrinsic viscosities between the sRAGE samples in the presence and absence of calcium. In the absence of calcium, the IV of sRAGE is approximately 0.08 dl/g. This value is much greater than that expected for proteins, which typically have IV values in the order of 0.03 dl/g: as observed for the BSA monomer. This immediately suggests that the sRAGE structure deviates from that of globular proteins. The Rh of the apo-protein is calculated to be approximately 3.60 nm. In the presence of calcium, the intrinsic viscosity of sRAGE shows a decrease of approximately 30% to 0.06 dl/g. Not only is this value still relatively high compared with the globular BSA, but it is also markedly different from the value obtained for sRAGE in the absence of calcium. Correspondingly, the Rh is also decreased from 3.60 to 3.24 nm, a change of approximately 10%. In order to determine the repeatability and significance of the IV changes, statistical analyses were carried out on a series of 10 replicate measurements of BSA. The %RSD between the 10 BSA measurements is just 3%, so a 30% shift in IV can be considered significant and not associated with experimental errors. The significant differences in the intrinsic viscosities of sRAGE in the presence and absence of calcium are likely to reflect a change in structure. A decrease in IV in the presence of calcium suggests an increase in molecular density and thus a conformational change of the protein that results in a more tightly folded structure. These observations are supported by other measurements performed on sRAGE. Temperature trend DLS measurements of the sample show an increase in melting point in the presence of calcium. This suggests a strengthening of the intramolecular forces that hold the protein structure together and is consistent with a tighter, more rigid conformation being formed (figure 2A). In addition, tryptophan fluorescence measurements show an increase in fluorescence in the presence of calcium. This is another indicator of a conformational change within the molecule (figure 2B).
The only other difference that remains unexplained is the apparent increased molecular weight of sRAGE in the absence of calcium. In the presence of calcium, the measured molecular weight is very close to the expected value; however, it increased in the absence of calcium. It is believed that in the absence of calcium, where the structure is more open, hydrophobic regions are exposed to the solvent. This leads to the association of acetonitrile with the protein that leads to a decrease in the apparent dn/dc of the sRAGE resulting in a higher measured molecular weight. Nevertheless, in this case, the measured molecular weight clearly indicates that this protein is in its monomeric form.
Conclusions
In this application note, the molecular weight and intrinsic viscosity of the protein sRAGE was successfully measured with multi-detector SEC in the presence and absence of calcium. Intrinsic viscosity measurements showed a decrease in IV in the presence of calcium suggesting a conformational change in the structure of the protein. This data was in agreement with other data produced by the Molecular Structure Group at the IBMC. The multi-detector SEC work was performed on a Viscotek TDAmax system with UV, RI, light scattering and intrinsic viscosity detectors.Malvern provides the materials and biophysical characterization technology and expertise that enables scientists and engineers to investigate, understand and control the properties of dispersed systems. These systems range from proteins and polymers in solution, particle and nanoparticle suspensions and emulsions, through to sprays and aerosols, industrial bulk powders and high concentration slurries. Used at all stages of research, development and manufacturing, Malvern’s instruments provide critical information that helps accelerate research and product development, enhance and maintain product quality and optimize process efficiency. Our products reflect Malvern’s drive to exploit the latest technological innovations. They are used by both industry and academia, in sectors ranging from pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals to bulk chemicals, cement, plastics and polymers, energy and the environment. Malvern systems are used to measure particle size, particle shape, zeta potential, protein charge, molecular weight, mass, size and conformation, rheological properties and for chemical identification, advancing the understanding of dispersed systems across many different industries and applications. www.malvern.com Material relationships http://www.malvern.com/en/ portal@malvern.com






